Steam Methane Reforming, SMR, ANSYS Fluent CFD Simulation
$120.00 $60.00 Student Discount
- This product numerically simulates the Steam Methane Reforming (SMR) using ANSYS Fluent software.
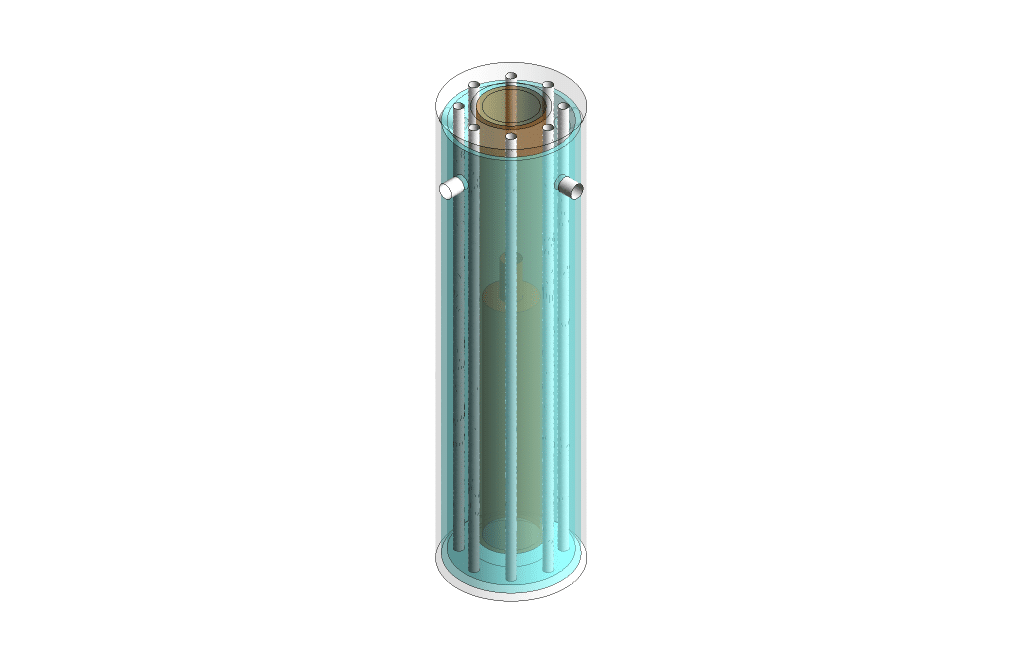
- We design the 3-D model using the Design Modeler software.
- We mesh the model with ANSYS Meshing software; the element numbers are 1651814.
- We use the Species Transport model to define the chemical reactions.
To Order Your Project or benefit from a CFD consultation, contact our experts via email (info@mr-cfd.com), online support tab, or WhatsApp at +44 7443 197273.
There are some Free Products to check our service quality.
If you want the training video in another language instead of English, ask it via info@mr-cfd.com after you buy the product.
Description
Description
In this project, we present the CFD simulation of the Steam Methane Reforming (SMR) using ANSYS Fluent software.
Steam Methane Reforming (SMR) is a hydrocarbon fuel processing technology for hydrogen production. SMR includes endothermic reactions in which methane reacts with steam on a catalyst to produce hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and carbon dioxide.
According to the first and second reactions, methane reacts with steam, by participating carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide is produced indirectly. However, according to the third reaction, methane reacts with steam, to produce carbon dioxide directly.
The SMR plant construction consists of a heating chamber containing reforming tubes. The burner generates heat in the heating chamber and the hydrogen produced is released through the gas exhausts.
Several types of SMR reactors are available in the industry. In this project, we model the sleeve type SMR.
Methodology
First, we modeled the SMR plant geometry in Design Modeler software. Then, we meshed the model using ANSYS Meshing software, and 1651814 elements were generated. Finally, we simulated the steam methane reforming process in ANSYS Fluent software.
In the SMR plant, several electrochemical reactions occur. Therefore, we used the Species Transport model. Then, we defined three reactions for the reforming tubes and one reaction for the thermal chamber.
In addition, we defined the porous medium in the reacting tubes as a catalyst.
Conclusion
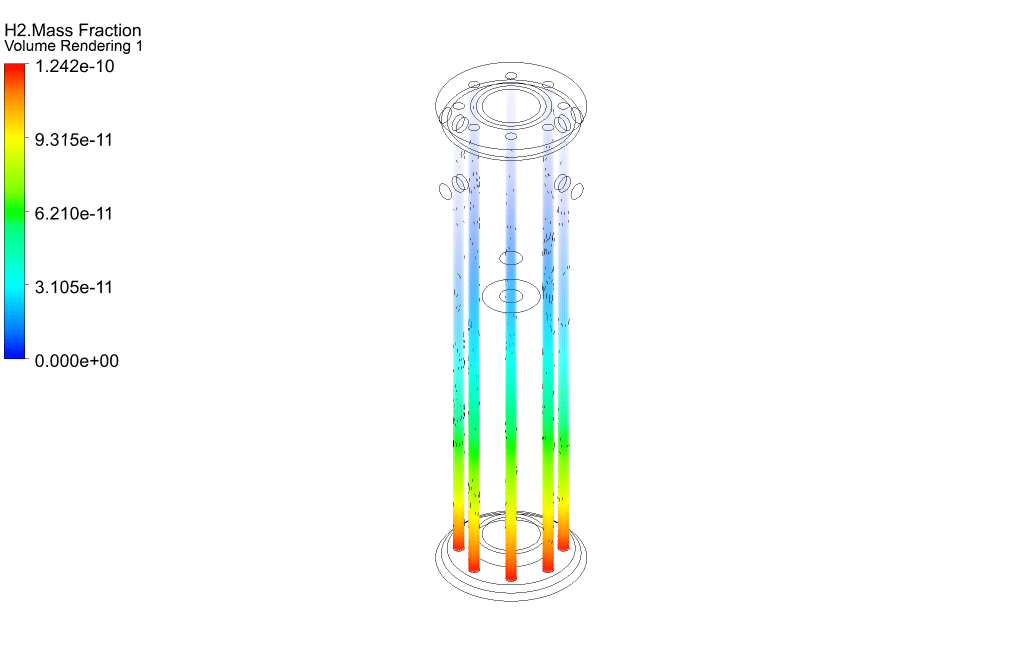
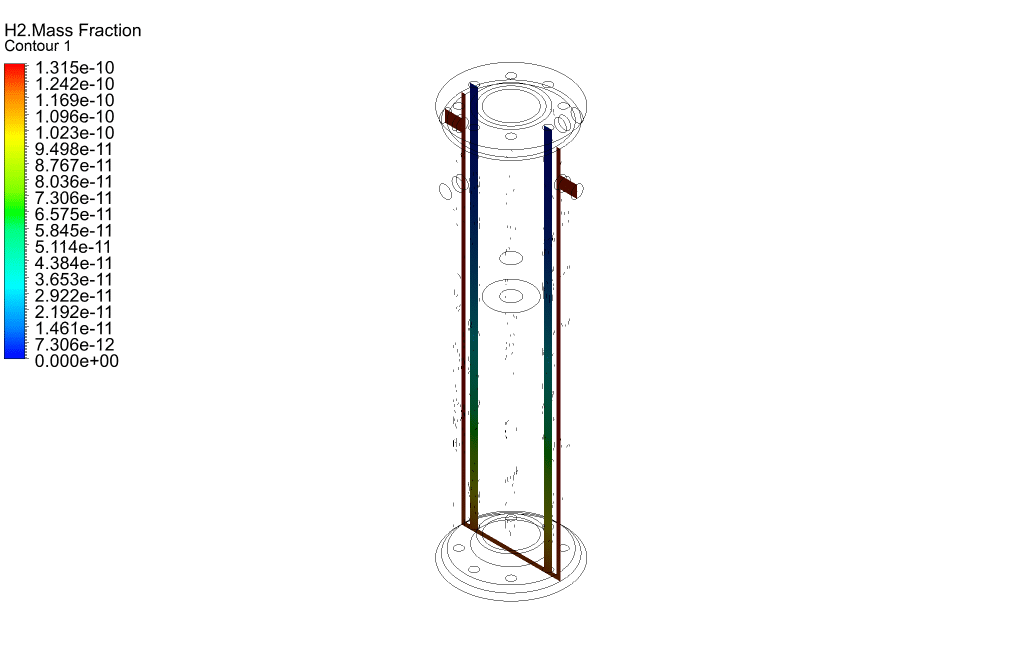
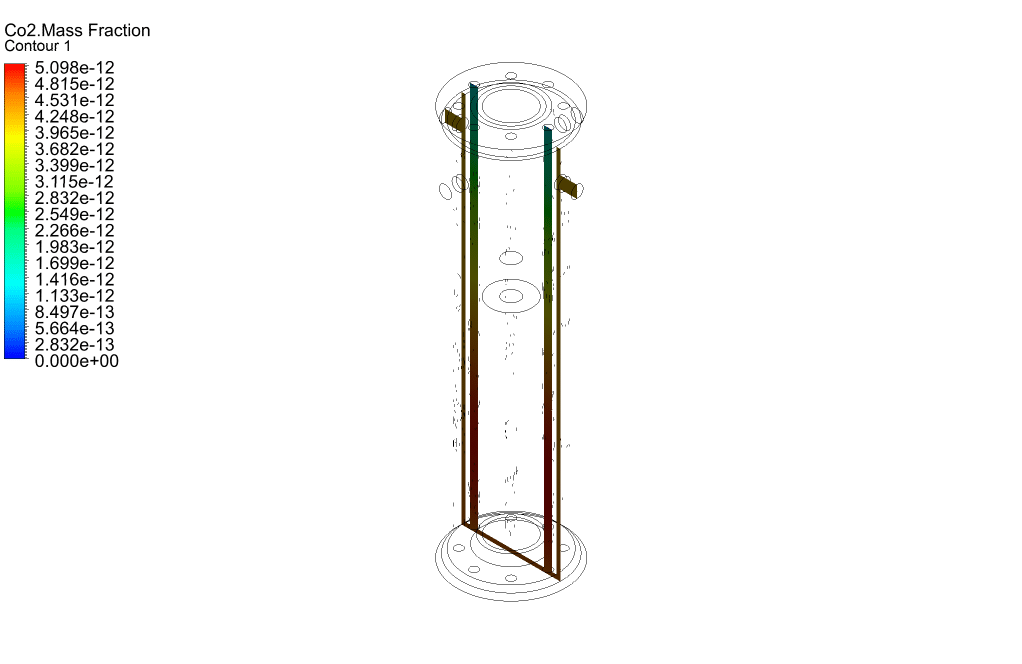
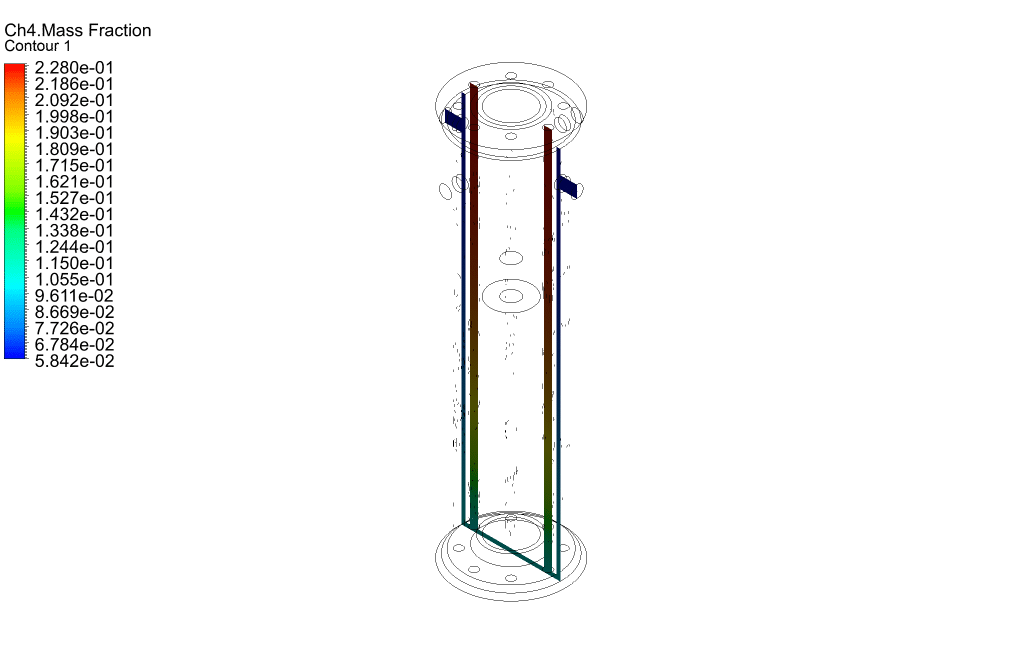
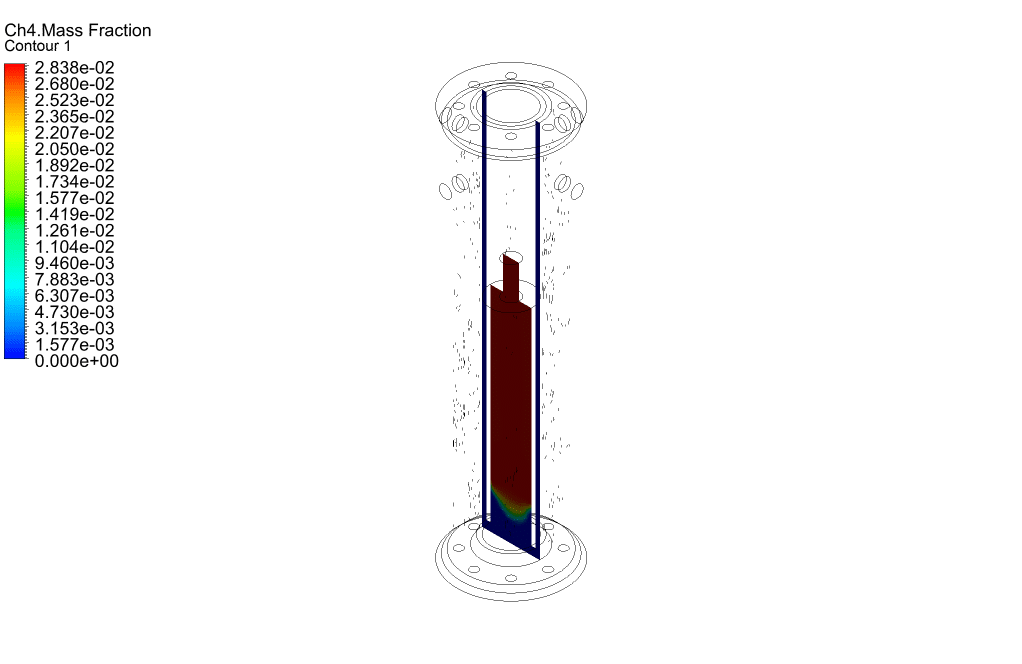
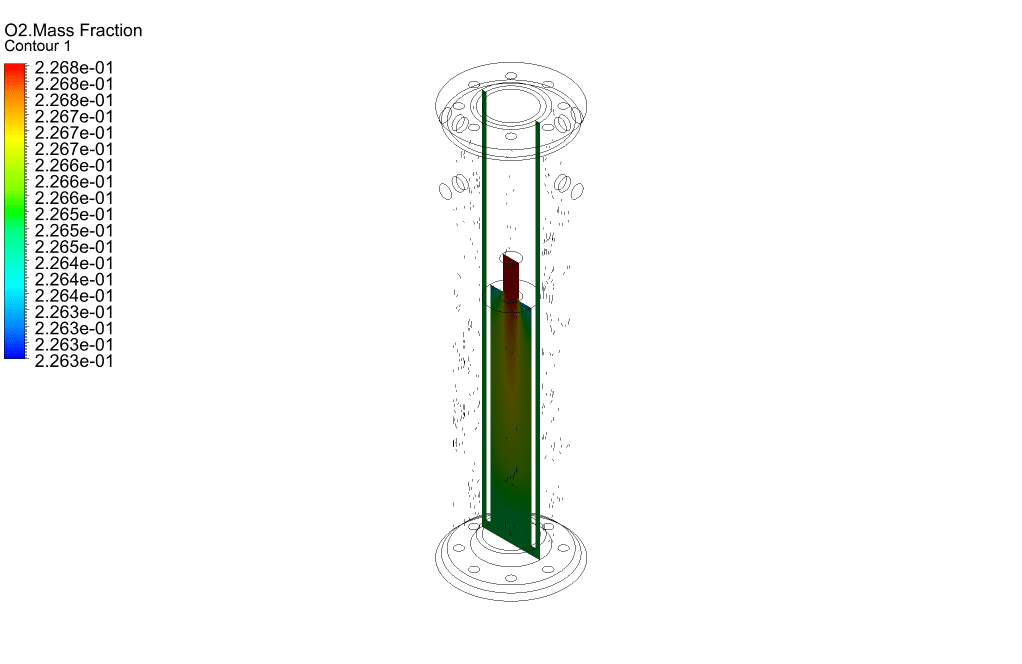
Finally, we study the distribution of species participating in electrochemical reactions. Therefore, we obtained mass fraction contours of different species including H2, CO, CO2, CH4, and O2.
The results show that methane was consumed in the reacting tubes and the hydrogen was produced and released. So, we conclude that the present SMR system is working properly.

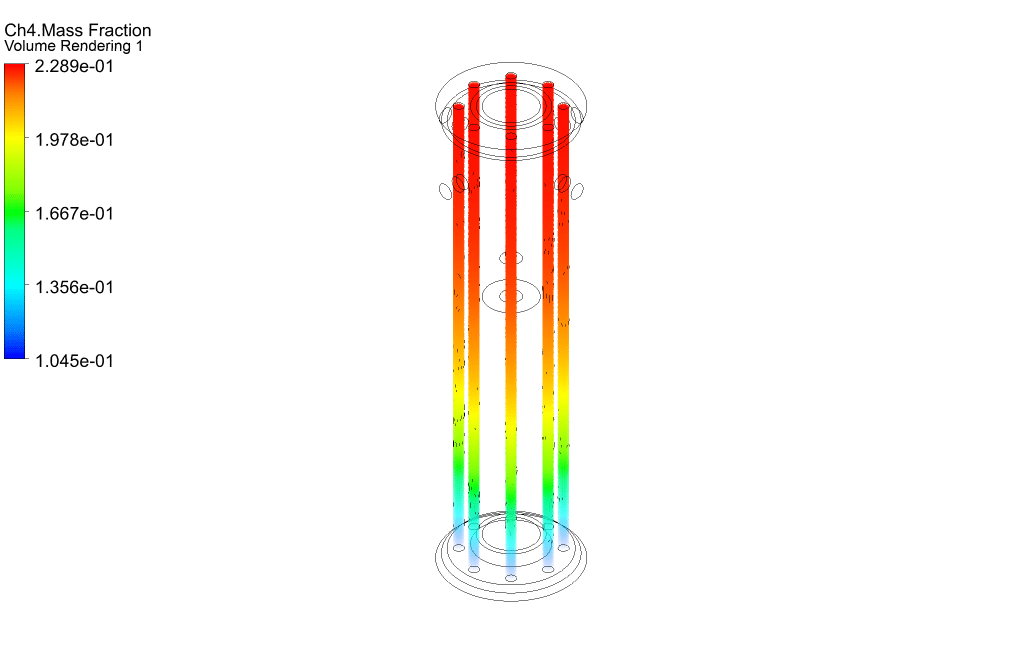


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.