Discrete Phase Model (DPM): Turbulent Dispersion
Introduction
By entering particles in a turbulent eddy, they try to follow it when they pass through the eddy. In this article, we aim to investigate two turbulent dispersion model available in Ansys Fluent software.
- Stochastic Tracking
- Cloud Tracking
Stochastic Tracking
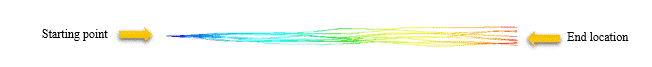
Stochastic tracking illuminates the local instantaneous turbulent velocity fluctuations and their impact on particle trajectories.
It complements random turbulent dispersion to each particle track. Tracks that start from the same point can be different at the final location.
However, it requires a large number of stochastic tries to achieve a statistically significant result.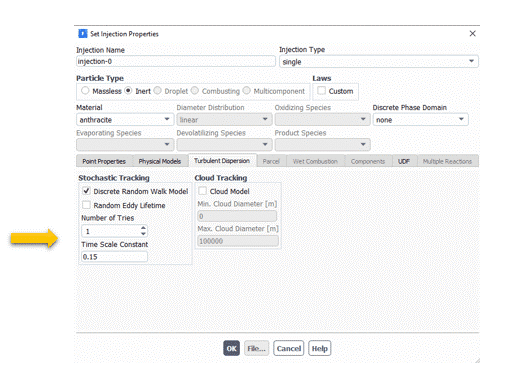
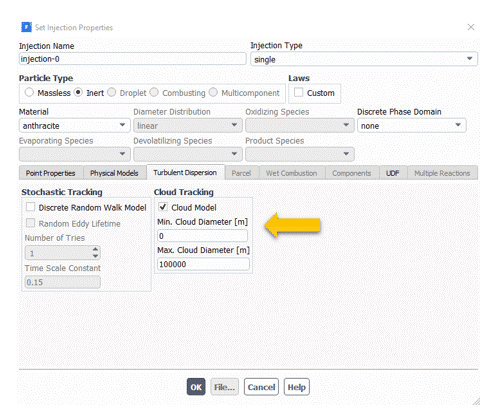
Cloud Tracking
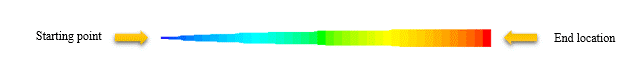
Cloud tracking uses statistical methods to track the turbulent dispersion of particles to calculate a mean trajectory.
The mean trajectory is calculated from the collective average of the equation of motion for the particles. A Gaussian probability density function represents the distribution of particles inside a cloud.
In cloud tracking, the local variations in the flow get averaged inside the particle cloud. It has a smooth distribution of particle coupling source terms. Each particle diameter requires its cloud trajectory calculation.
This tracking model only can be used in solving the steady-state continuous phase.
It should be noted that different cloud trajectory calculations will be done for each diameter size.



Comments (0)