Adhesion effect on a self-cleaning material (porous medium) CFD Simulation, ANSYS Fluent
$100.00 $50.00 Student Discount
- This problem simulates Adhesion effect on a self-cleaning material (porous)using Ansys Fluent software.
- The 2-D geometry is designed in Design Modeler software.
- Ansys Meshing software is used to generate the mesh; the element number equals 105,000.
- In this project, the Hydrophilicity and hydrophobicity of surfaces is simulated using the VOF
- How the flow pattern near a hydrophobic surface and near a hydrophobic surface is well modeled in this project.
To Order Your Project or benefit from a CFD consultation, contact our experts via email (info@mr-cfd.com), online support tab, or WhatsApp at +44 7443 197273.
There are some Free Products to check our service quality.
If you want the training video in another language instead of English, ask it via info@mr-cfd.com after you buy the product.
Description
Adhesion effect on a self-cleaning material (porous medium) CFD Simulation, ANSYS Fluent
Description
Self-cleaning materials are porous structures with hydrophobic properties. Self-cleaning materials are substances that have the ability to clean themselves without human intervention or the use of chemical agents. These materials typically utilize two main mechanisms:
- Lotus Effect: These materials have an extremely hydrophobic surface that causes water droplets to easily roll off the surface, carrying away contaminants.
- Photocatalytic: In this method, materials (usually containing titanium dioxide) create a chemical reaction in the presence of sunlight that breaks down organic pollutants.
These materials are used in various industries including construction (for windows and building facades), automotive manufacturing, and textile production. The porosity of these materials at micro and nanoscales creates a rough surface. This roughness, combined with hydrophobicity, allows water droplets to easily roll off the surface, carrying away contaminants. In fact, the combination of porosity and hydrophobicity increases the water contact angle with the surface, leading to self-cleaning properties. This mechanism is inspired by the leaves of plants like the lotus, which naturally remain clean. The porous structure traps air pockets, reducing the contact area between water and the surface, thus enhancing the self-cleaning effect.
Ansys Fluent software provides the VOF model, which is a homogeneous model, for two or multi-phase flows where all phases are continuous and have a defined interface. The main goal of this model is to find this specific interface. The VOF model uses a special discretization to discretize the volume fraction equation, which makes the interface between the phases well modeled. To use this model, it must be observed that the mesh size is very small in the places where we have an interface.
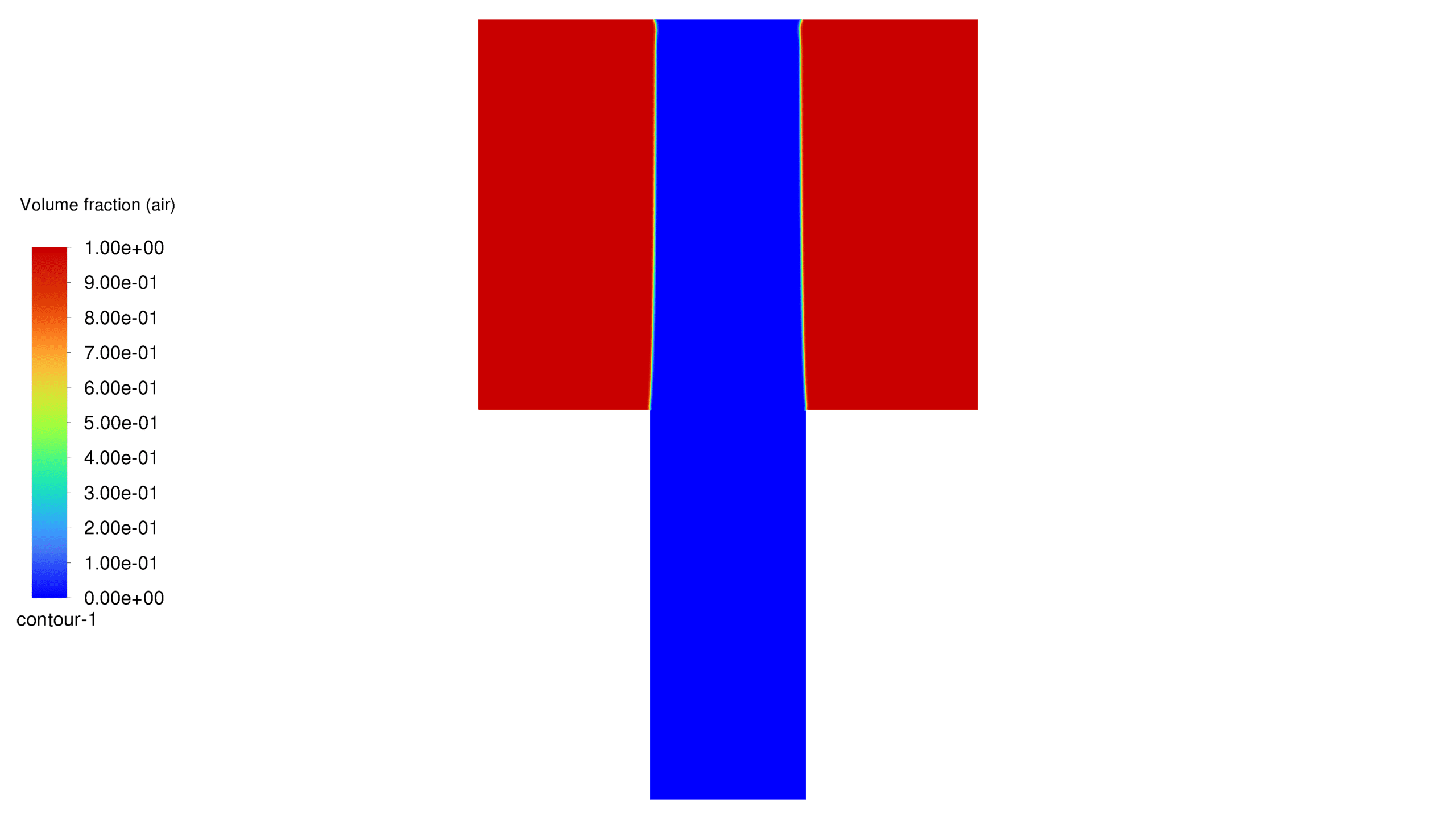
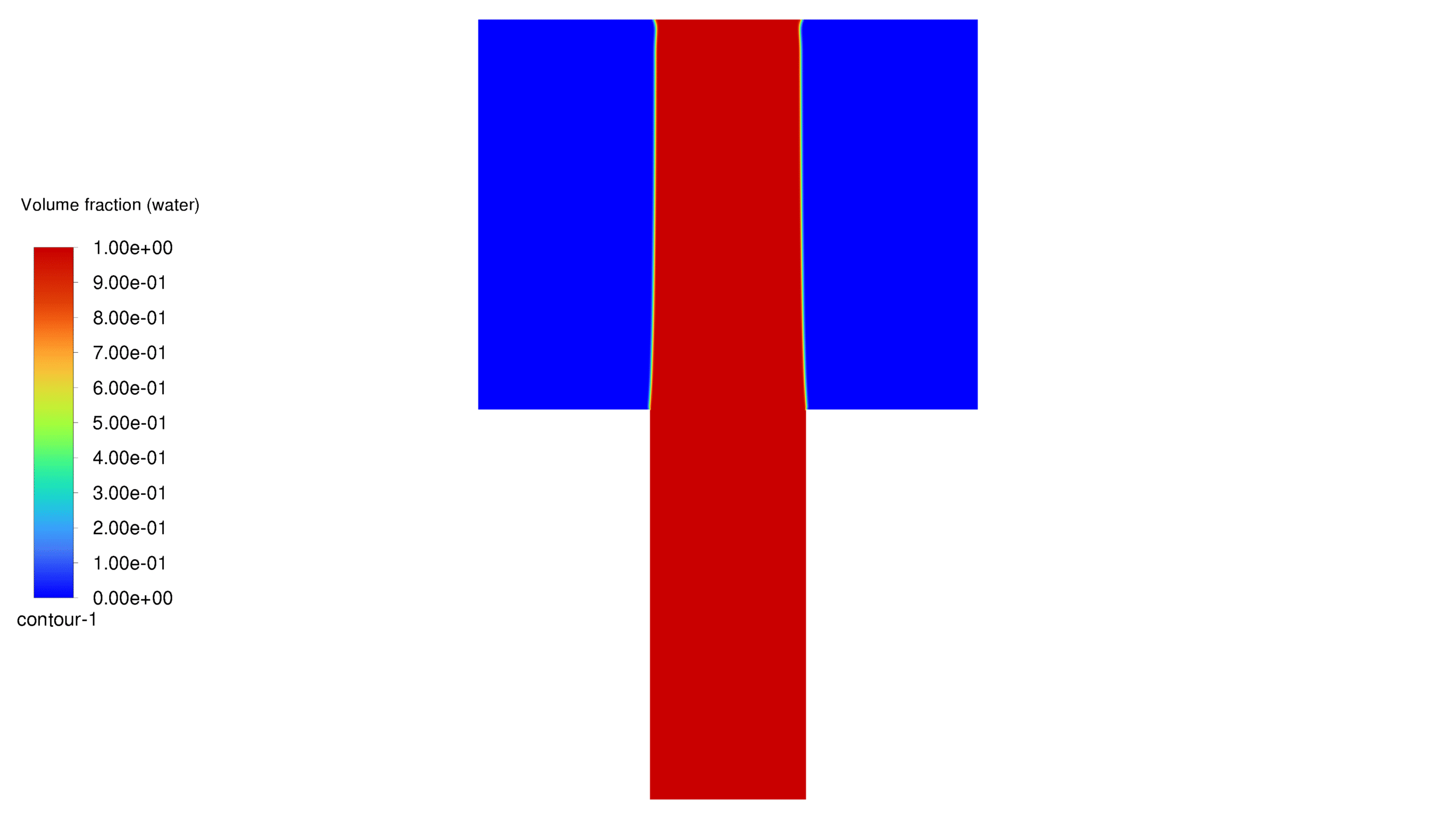
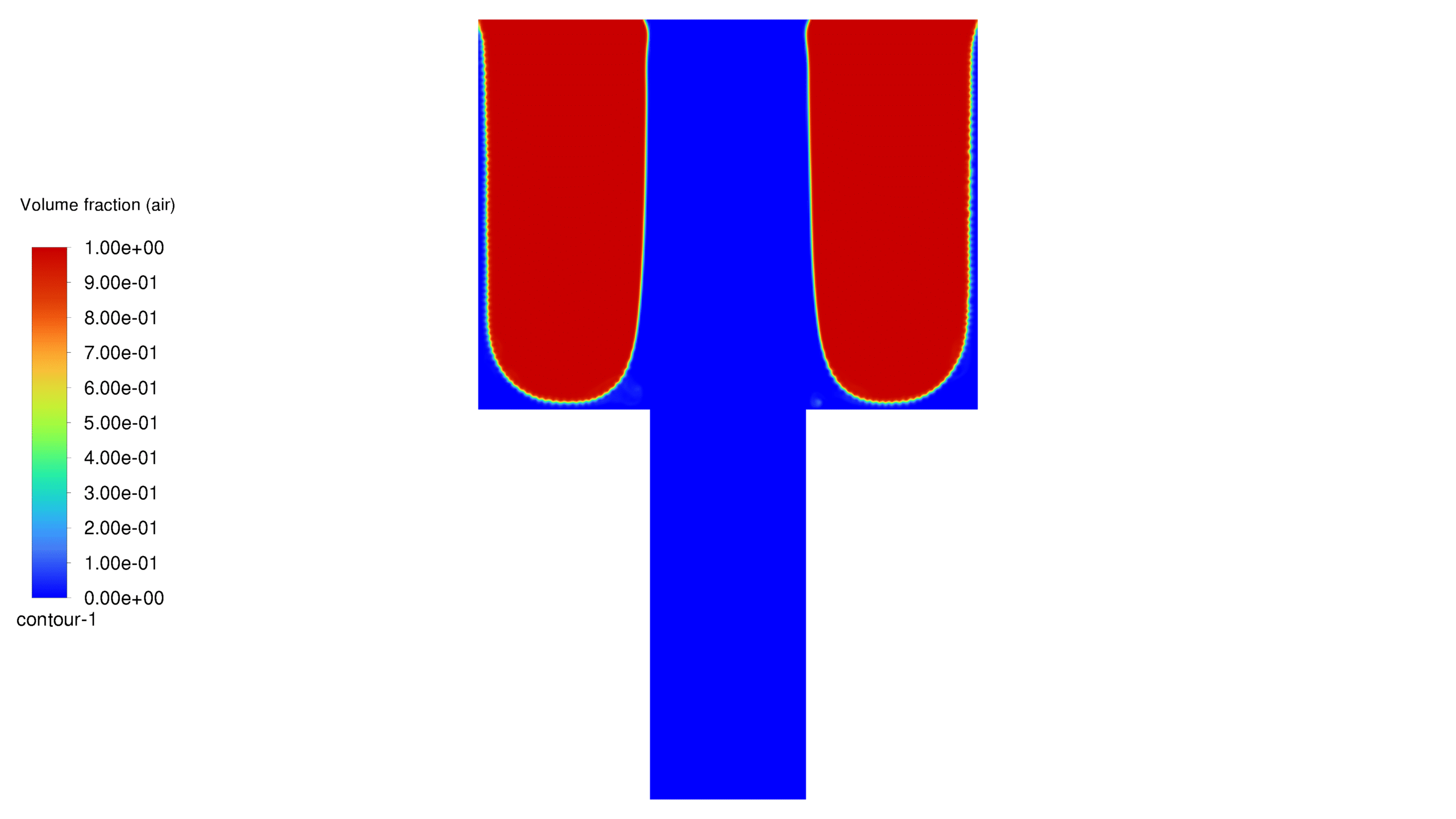
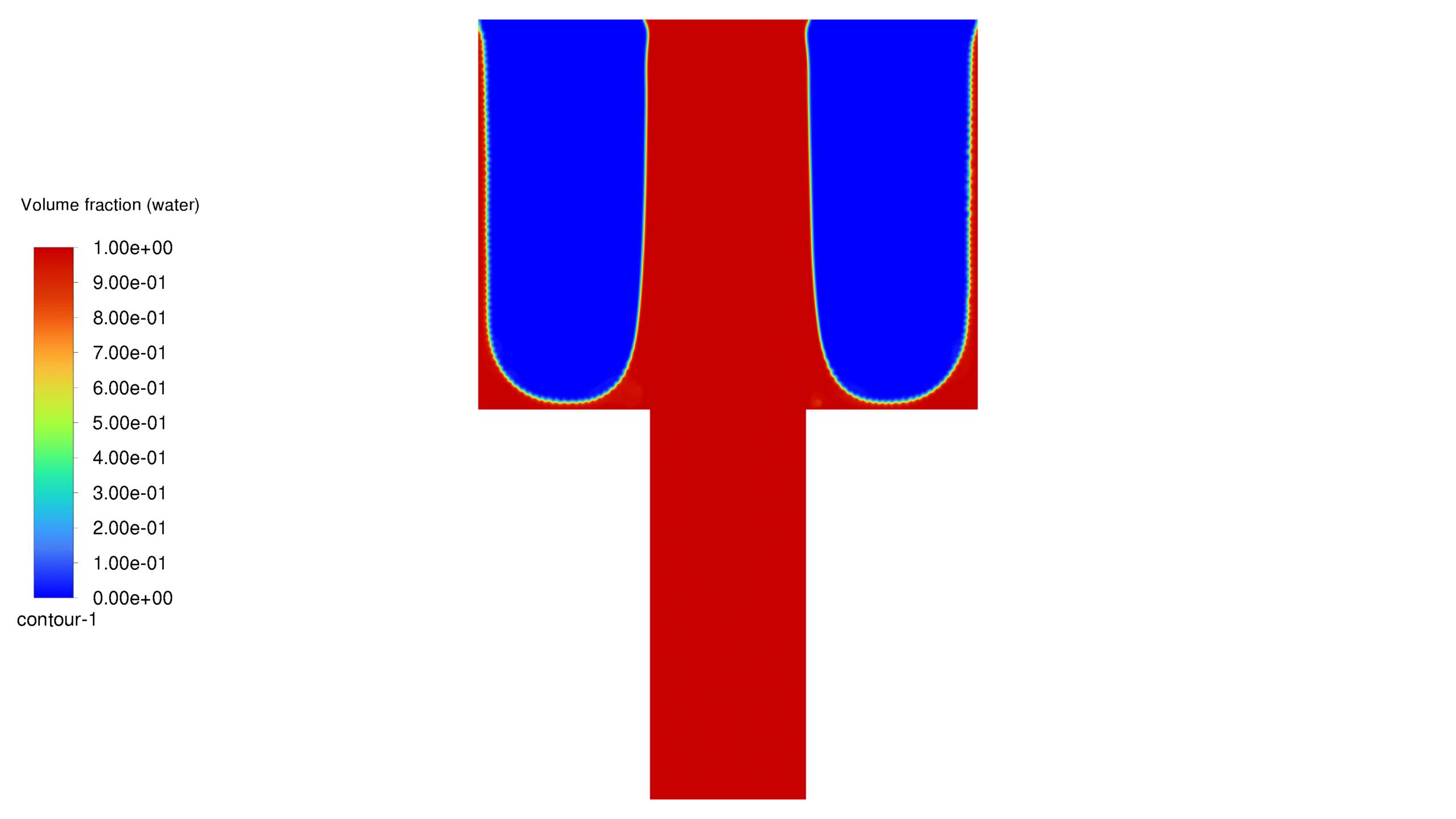
In this project, a porous medium has been considered, into which water is injected from the bottom. Two distinct cases of hydrophilic and hydrophobic wall conditions have been modeled with contact angles of 20 and 160 degrees, respectively. Furthermore, the dispersion pattern of water flow within the porous material has been effectively simulated. It should be noted that this project does not address the properties of self-cleaning materials or their molecular characteristics.
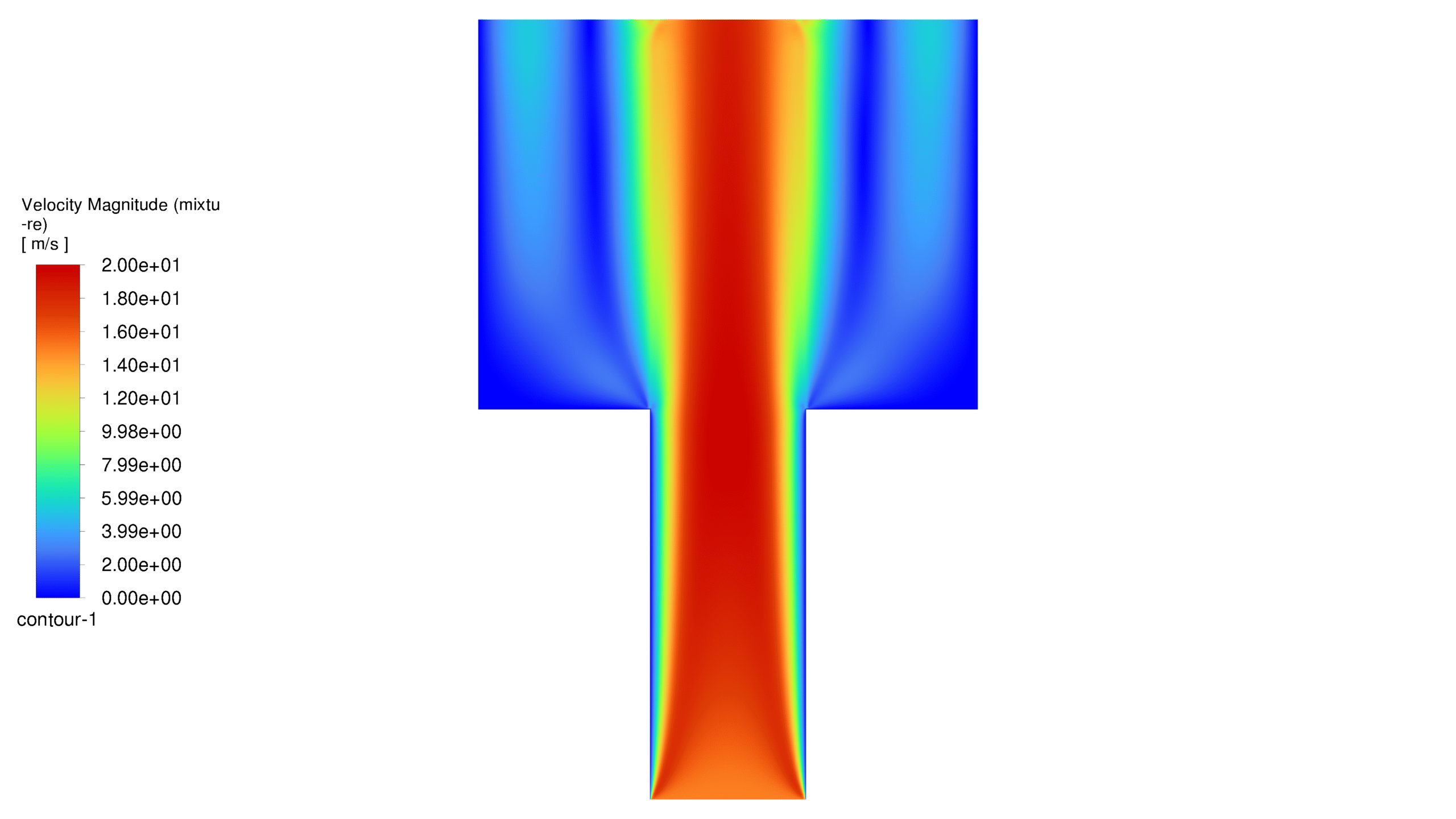
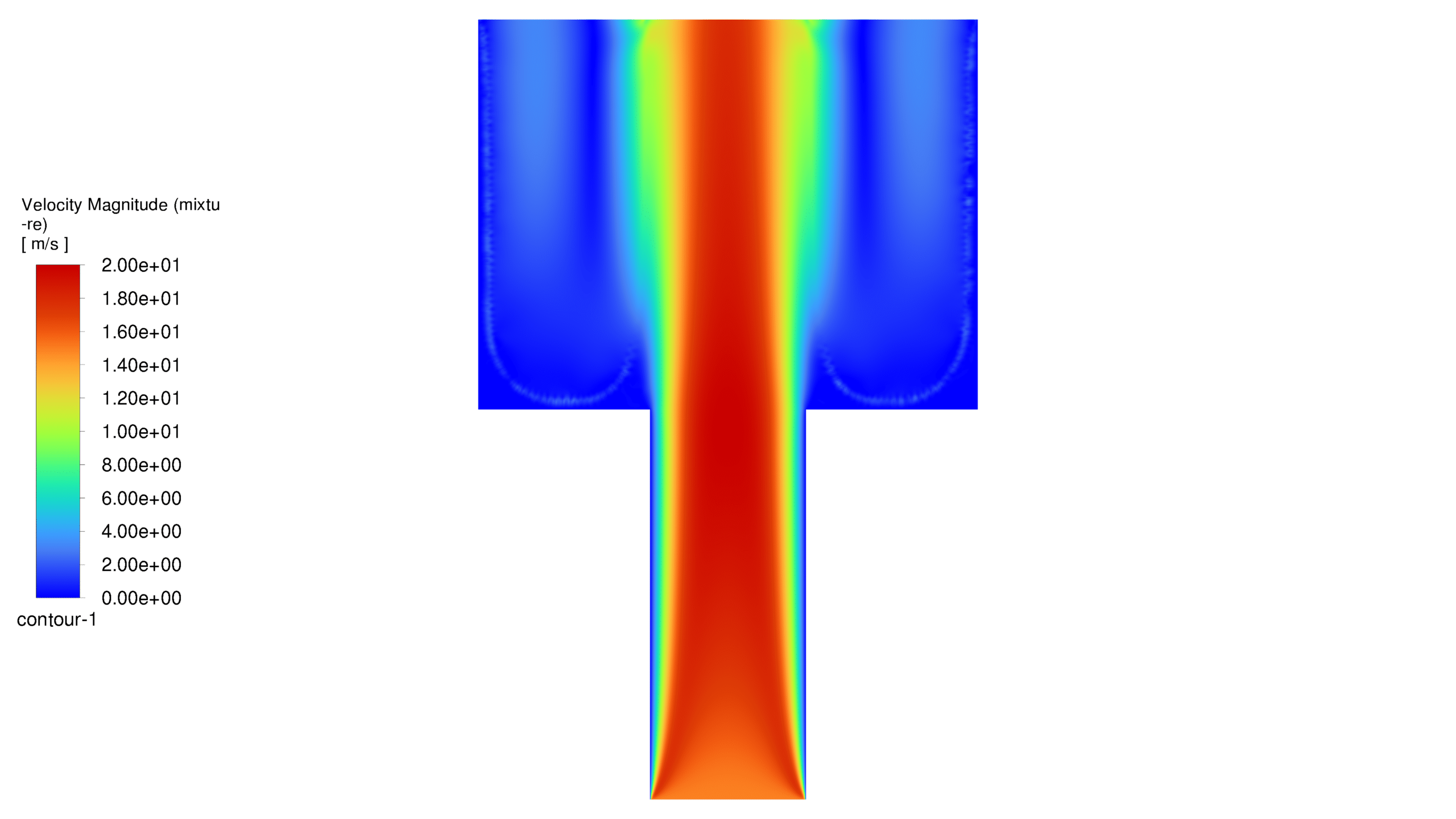
An inlet for water, 10 micrometers long, is placed at the bottom of the porous medium. The outlet is located at the top of the geometry. For simplicity, the project is solved in one plane of the real shape, i.e. in two dimensions. The water flow enters the geometry from the bottom and exits from the top. The flow spreads in different patterns depending on whether the walls are hydrophilic or hydrophobic.
CFD simulation methodology
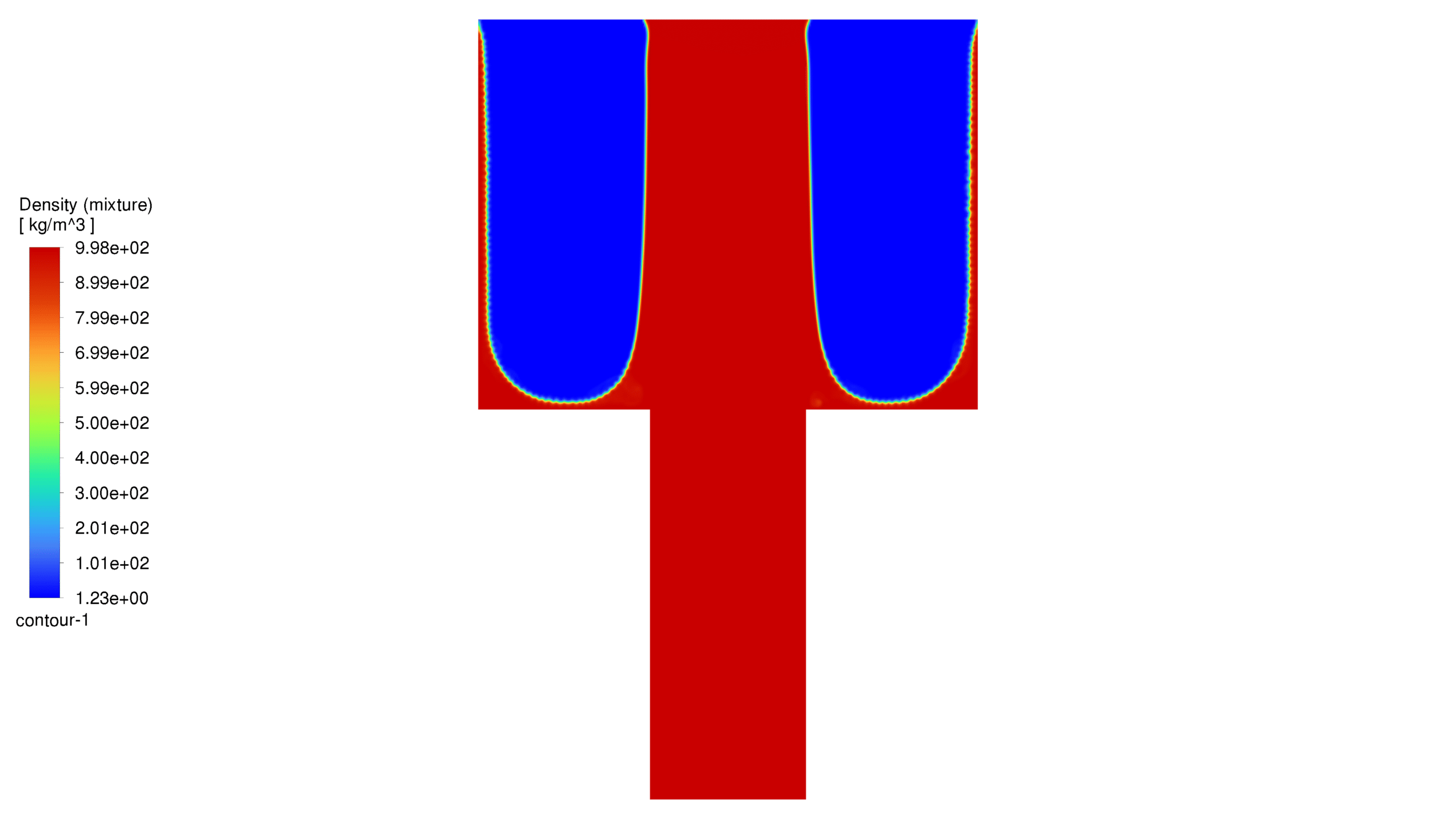
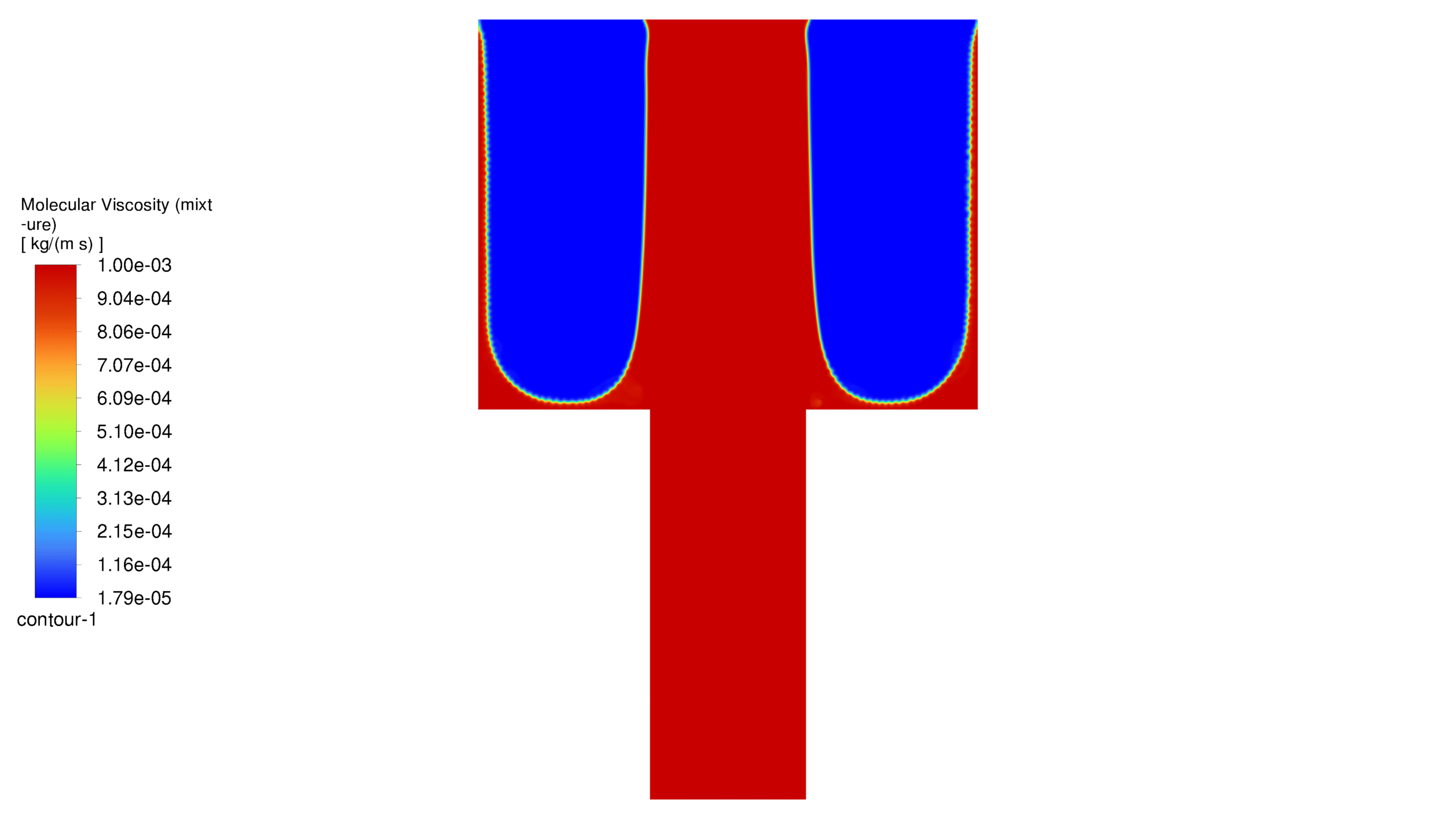
In this project, the geometry is generated in Design Modeler and meshed in ANSYS Meshing with 105,000 elements. The elements are structured. In this project, it is assumed that the flow is slow, and since the geometric dimensions are very small, the problem has been solved as laminar flow. For simulation, VOF multiphase flow model has been used. The project is two-phase and the phases are air and water. For the initial conditions, it is considered that the porous medium contains air and as soon as the solution starts, water flows from the corresponding inlet. It should be noted that the simulation is done transiently. In this project, the effect of gravity has been ignored. Please note that the contact angle between water and the walls is considered to be 160 degrees in the hydrophobic case and 20 degrees in the hydrophilic case. In this project, the fluid porosity is considered to be 0.5. It should be noted that water is injected into the porous medium at a speed of 15 meters per second.
Conclusion
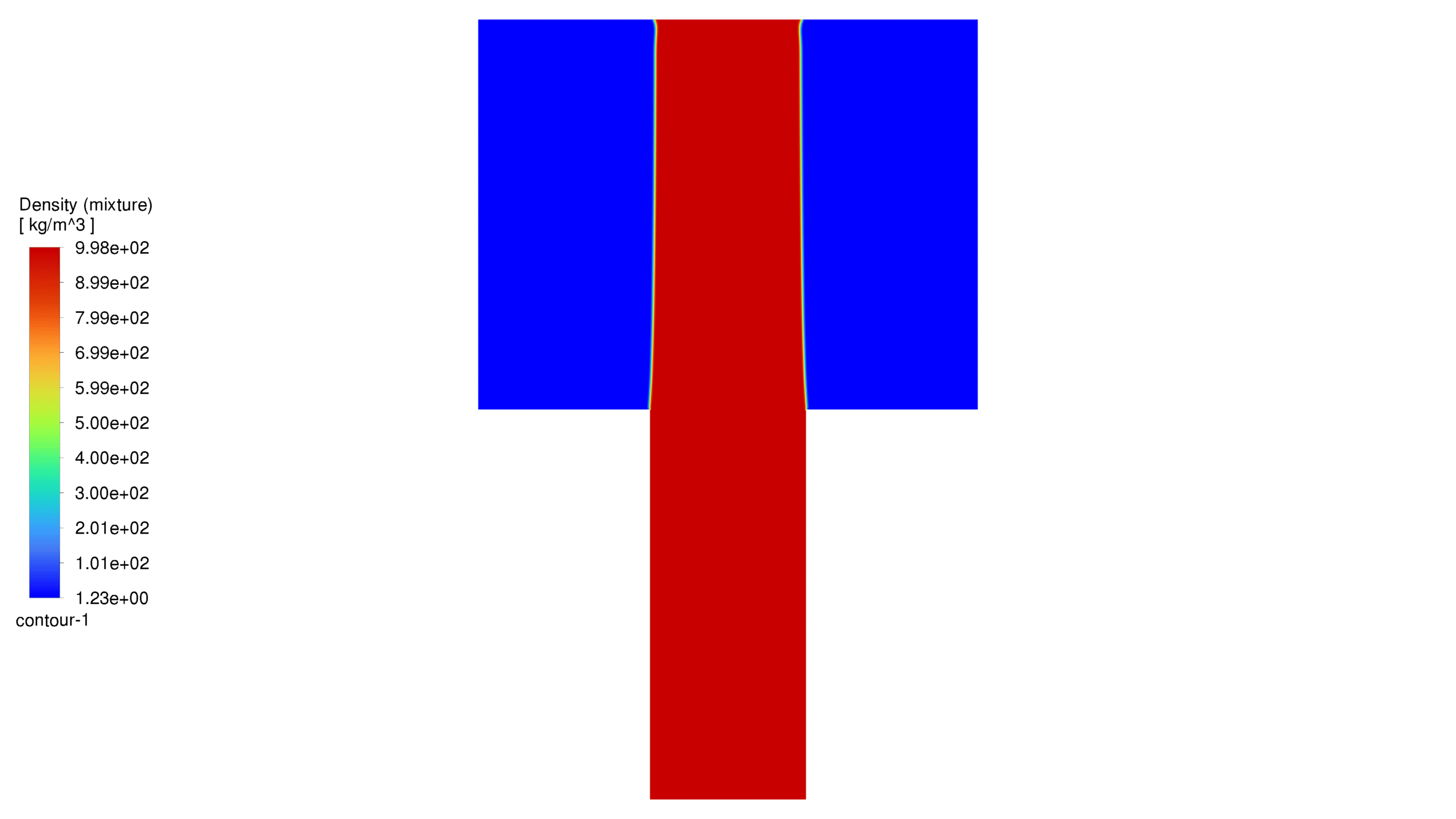
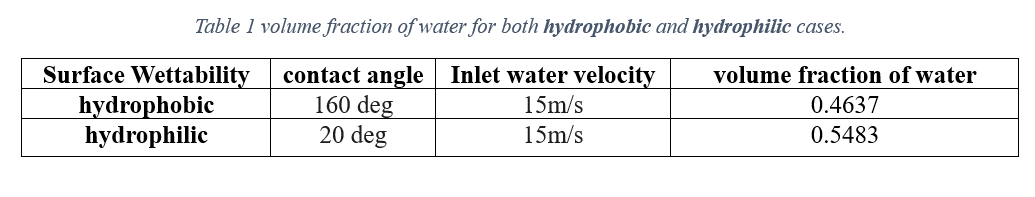
At the end of the solution process, two-dimensional contours related to pressure, velocity, viscosity, density, water volume fraction and air volume fraction were obtained for each case. The volume fraction of water for both hydrophobic and hydrophilic cases is listed in Table 1. As expected, a hydrophobic surface tends to retain less water, while hydrophilic surfaces lead to water remaining in close proximity to themselves.
Finally, for a better understanding, in each case an animation of how the water flows have been prepared. By comparing these two states, you gain a complete understanding of the hydrophilic and hydrophobic properties of a surface.




Reviews
There are no reviews yet.