Carbonate Cake Filtration ANSYS Fluent Tutorial
$120.00 $60.00 Student Discount
- The problem numerically simulates the Carbonate Cake Filtration using ANSYS Fluent software.
- The geometry is designed in a 2D model with the ANSYS Design Modeler software.
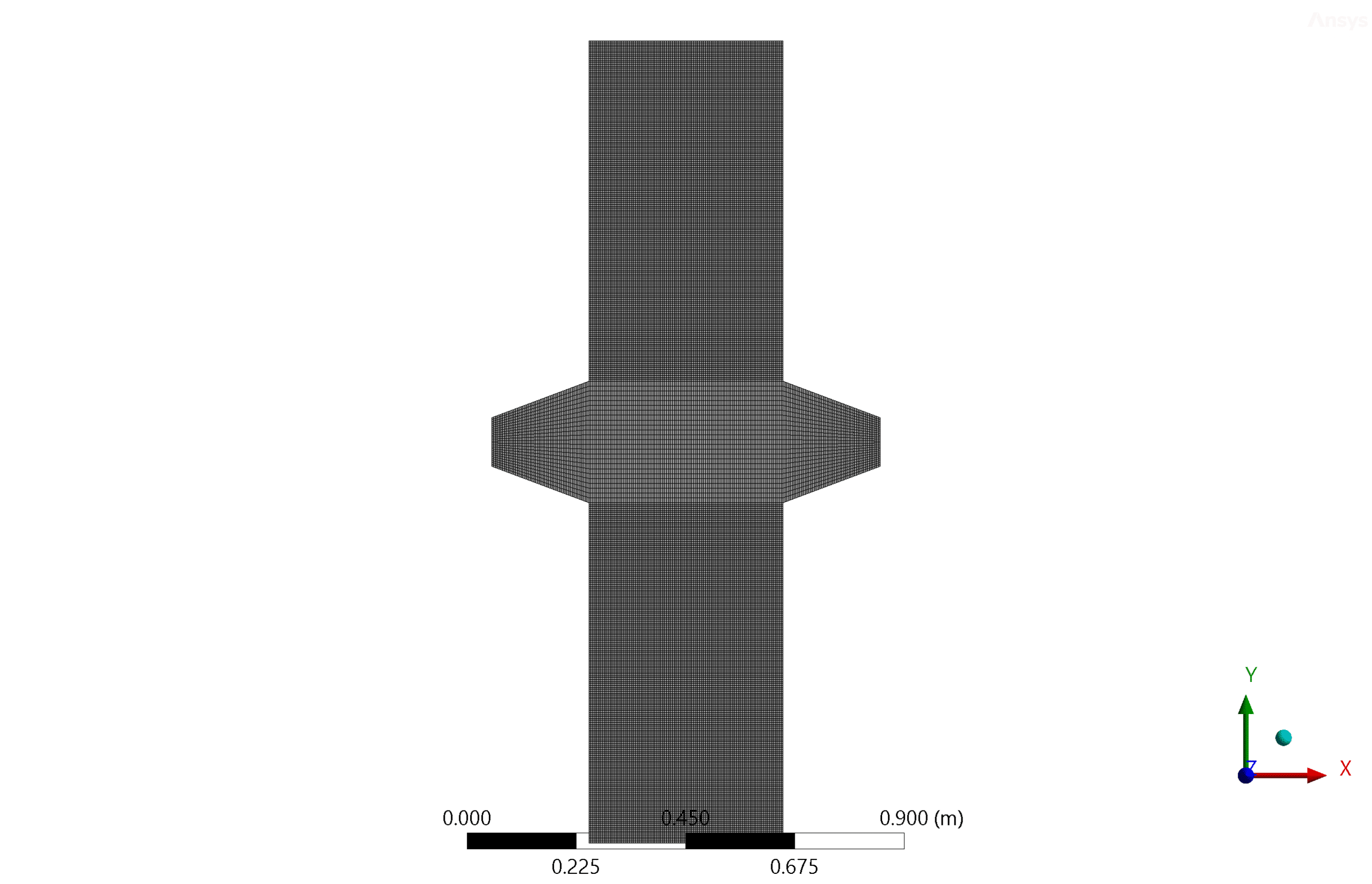
- We performed the structured mesh of the model with ANSYS Meshing software, and the element number equals 40,150.
- The Eulerian model was used to simulate the multiphase behavior of the solution.
- The project is solved in transient state.
To Order Your Project or benefit from a CFD consultation, contact our experts via email (info@mr-cfd.com), online support tab, or WhatsApp at +44 7443 197273.
There are some Free Products to check our service quality.
If you want the training video in another language instead of English, ask it via info@mr-cfd.com after you buy the product.
Description
Description
In this project, the filtration of carbonate dissolved in water is simulated. Filtration is a physical separation process that separates solid and liquid matter from a mixture using a filter medium that has a complex structure that only the liquid can pass through. Solid particles that cannot pass through the filter medium are called oversize.
This product is the fourth chapter of the Eulerian Multiphase Model Training Course.
Large particles may form a filter cake on top of the filter and may also block the filter mesh and prevent the fluid phase from passing through the filter.
The geometry of the present project is designed in Design modeler and meshed in ANSYS Meshing software. The mesh type is structured and the element number is equal to 40,150.
Carbonate Cake Filtration Methodology
The Eulerian multiphase model was used in this project to simulate the filtration of carbonate from water and cake filter layer formation. Carbon material was used to act as the filter, reducing the concentration of the carbonate material. Granular along with packed bed sub-model was activated to model the filtration and cake filter layer formation. The phase property model was used to obtain the granular temperature.
Drag, lift and virtual mass forces were also enabled between the phase pair of water and carbonate. The value of restitution coefficient between the solid materials (carbonate and carbon filter) is set equal to 0.9. Also, the filtration unit acts as a heat exchanger which reduces the temperature of the feed water.
Therefore, Ranz-Marshall model is used to calculate the heat transfer between the water and carbon filter, which can calculate the new temperature of each phase after their interactions.
Furthermore, energy equation is enabled to calculate the temperature change inside the domain. In addition, standard k-epsilon model is used to solve for the turbulent fluid equations. The present study is performed in transient format. 2D planar model is used to simulate the problem inside a two-dimensional domain.
Conclusion
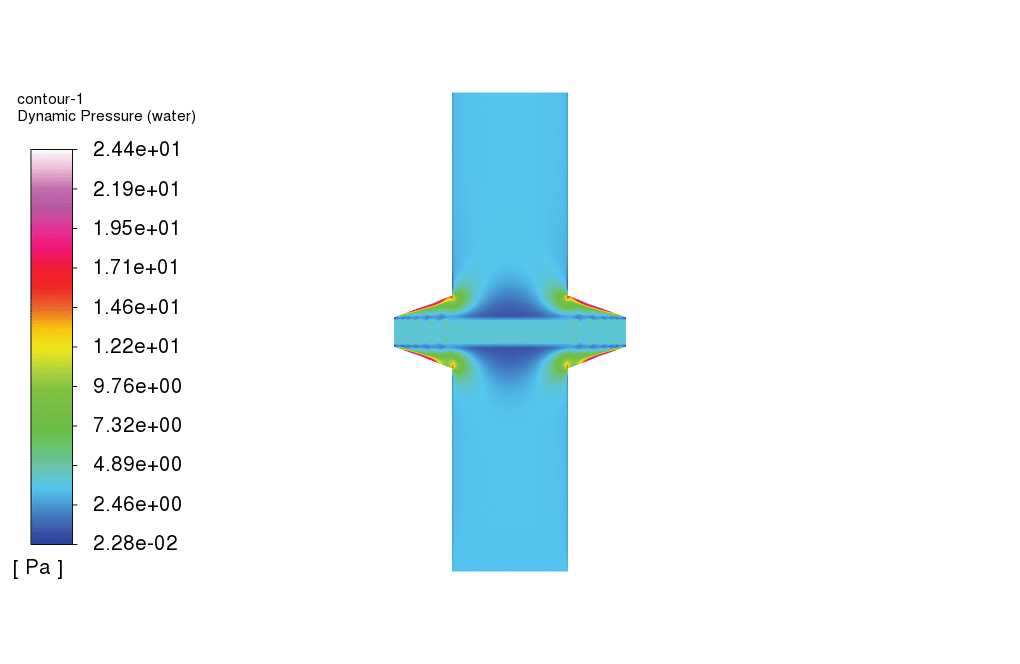
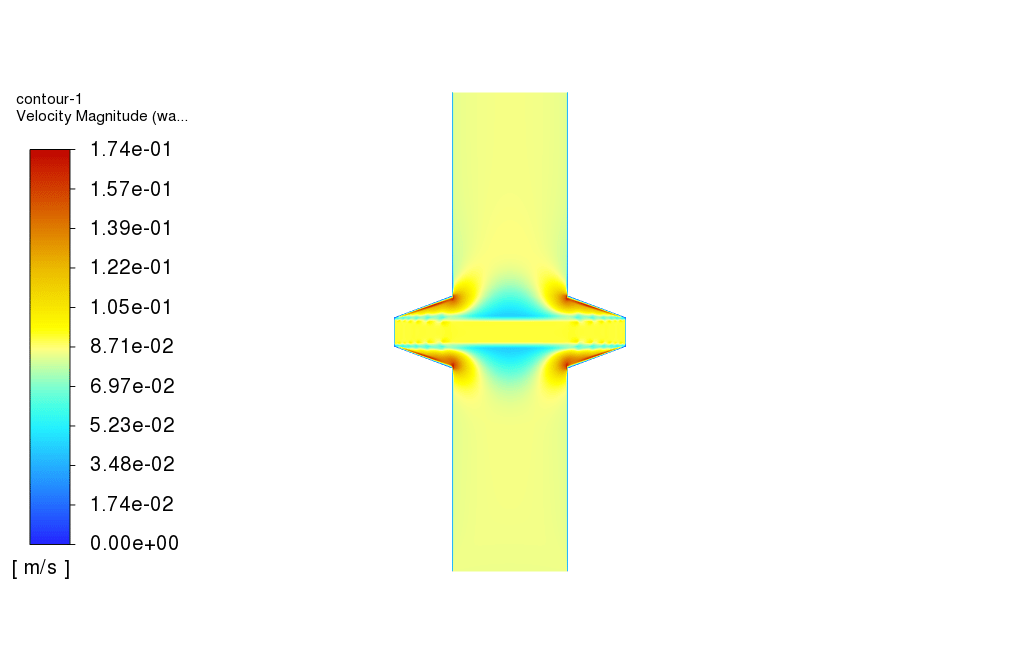
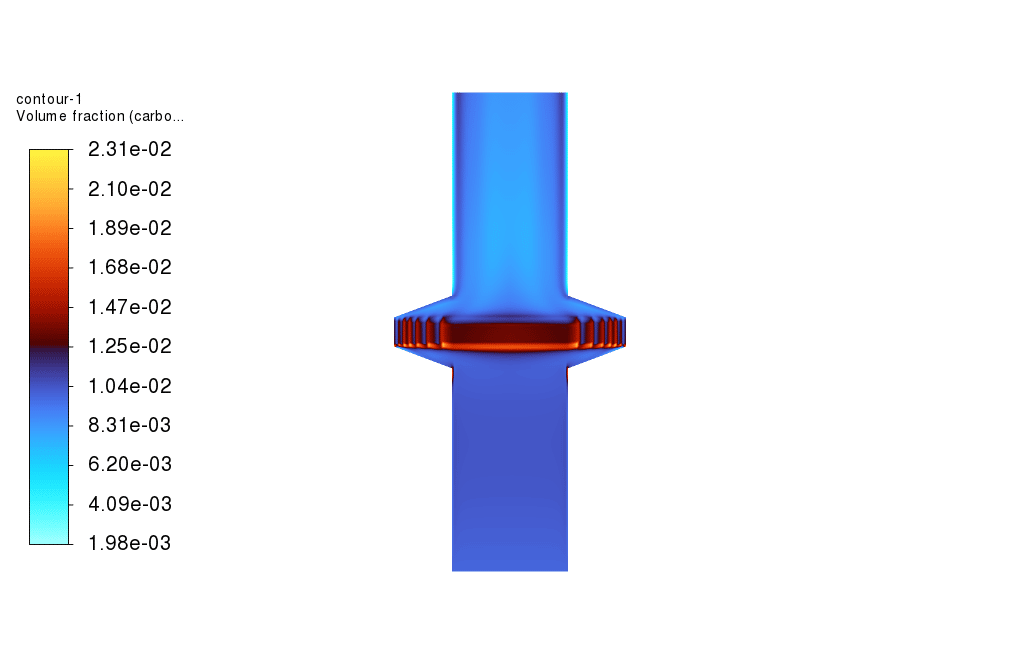
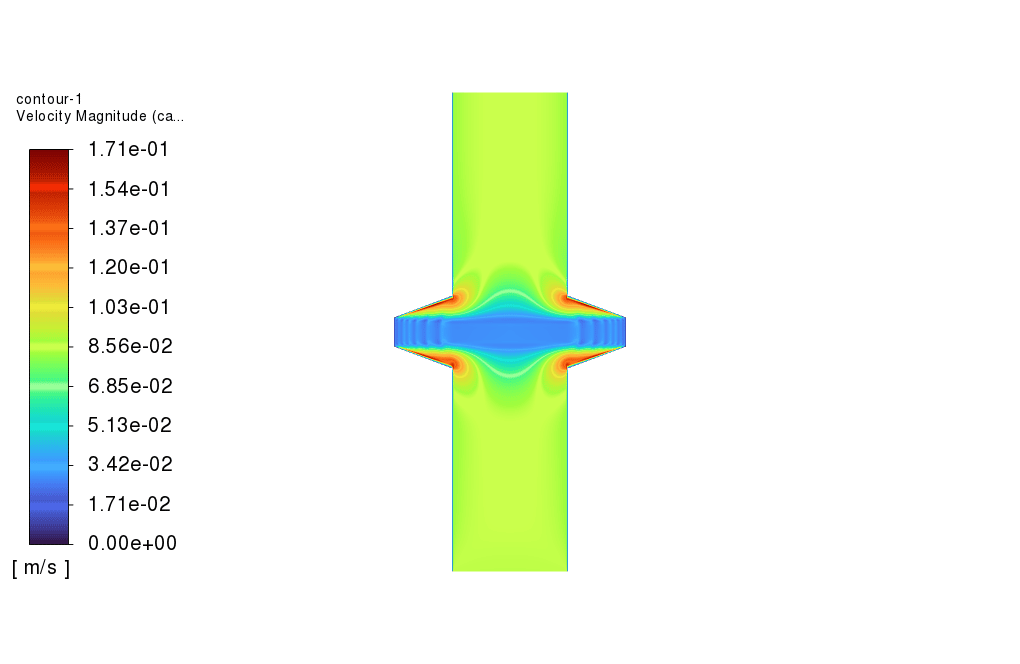
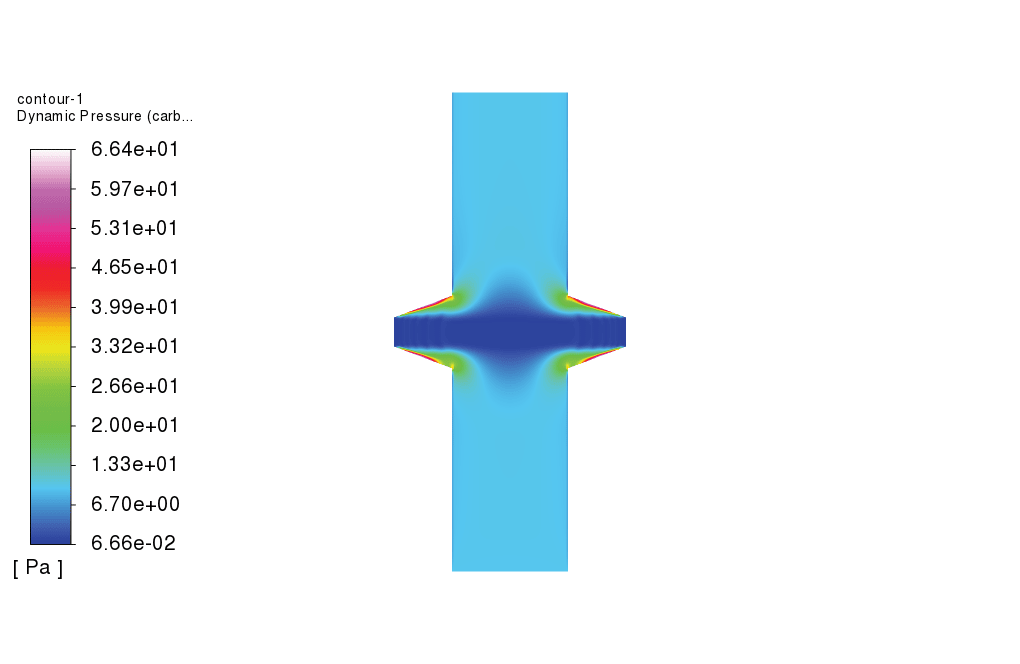
As observed in the obtained results, the carbon filter reduces the concentration of carbonate dissolved in the water. Also, the temperature of the feed water drops as it passes over the carbon filter. Furthermore, as shown in the plot for the carbonate volume fraction, the volume fraction of carbonate increases drastically just before the filter, which is a sign of cake filter layer formation over the carbon filter.

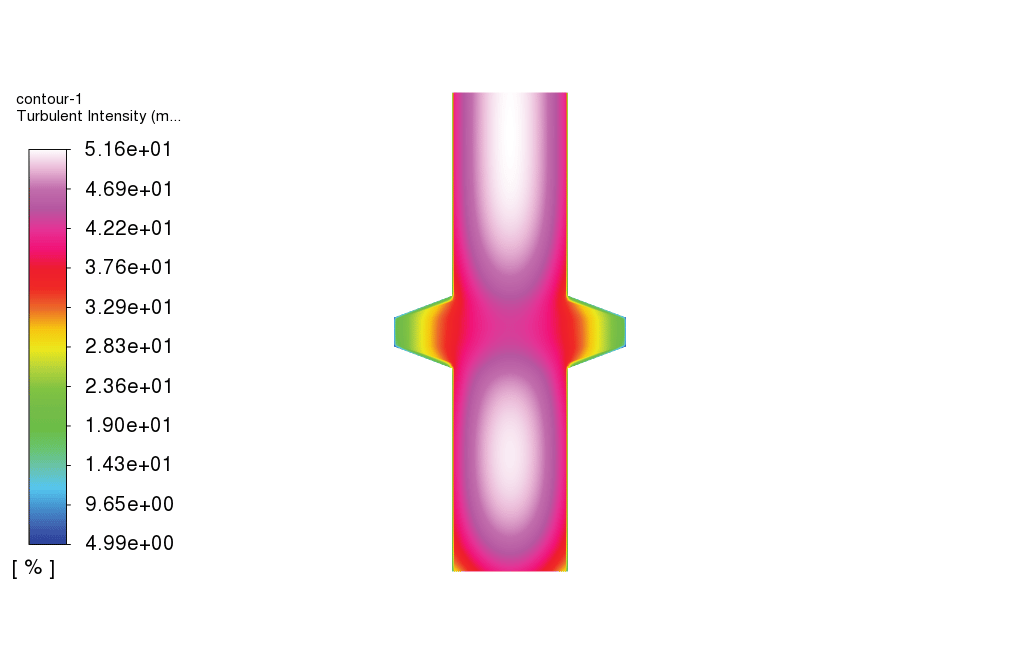
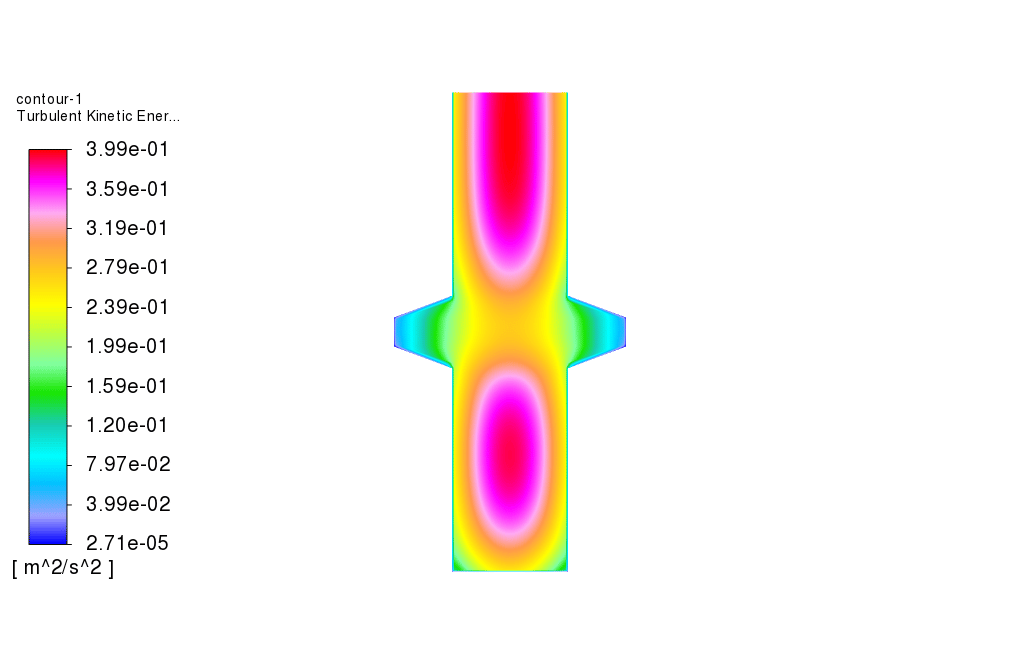



Reviews
There are no reviews yet.