horizontal fluidized bed dryer, Ansys Fluent CFD Simulation
$160.00 $80.00 Student Discount
- In this project, the evaporation of soil moisture in a fluidized bed was simulated using ANSYS Fluent.
- The geometry was created in SpaceClaim, and a mesh consisting of 22,000 elements was generated using ANSYS Meshing.
- The Eulerian model was chosen to simulate multiphase flow, and the species transport model was used to define the mixture in each phase.
- Evaporation was modeled using the evaporation-condensation method based on the Lee
To Order Your Project or benefit from a CFD consultation, contact our experts via email (info@mr-cfd.com), online support tab, or WhatsApp at +44 7443 197273.
There are some Free Products to check our service quality.
If you want the training video in another language instead of English, ask it via info@mr-cfd.com after you buy the product.
Description
Description
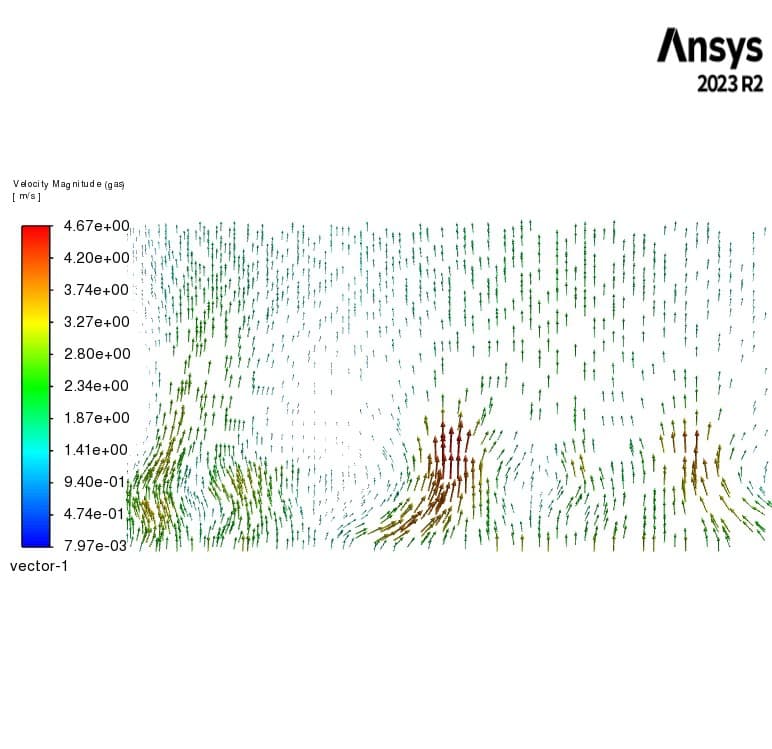
Solid particles, when small enough, can behave like a fluid in vertical flows. In other words, by applying an upward flow to a pool of sand with fine particles, the particles can become fluidized. This occurs when the drag force exerted by the fluid on the particles equals the gravitational force acting on them, causing the particles to levitate and behave like a fluid.
This phenomenon, known as fluidization, is used in several industrial applications. For example, it is employed to increase the residence time for burning waste biofuels and is also used in petroleum production with catalysts.
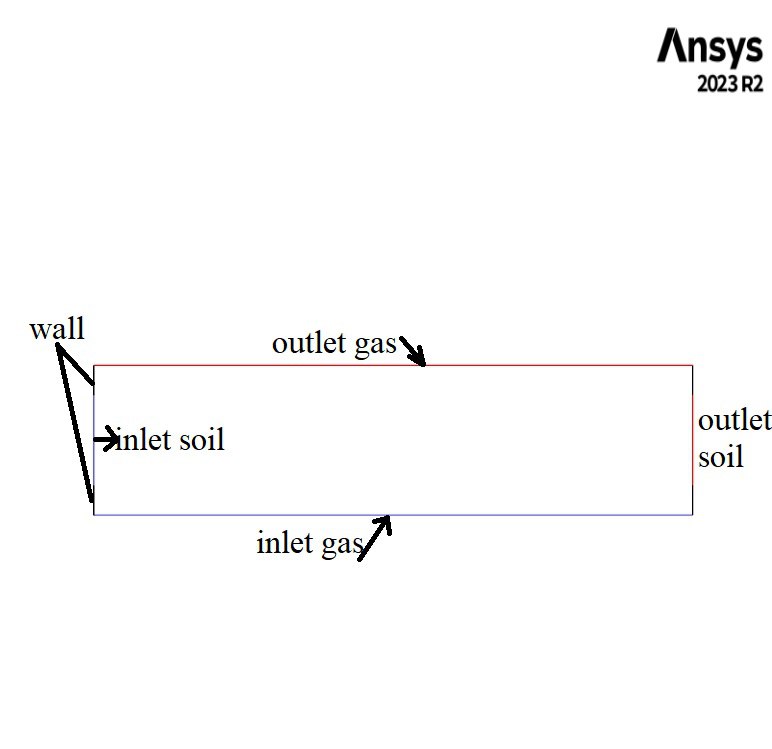
In this project, a horizontal fluidized bed is simulated with the purpose of drying incoming soil containing moisture. The soil enters the fluidized bed at a mass flow rate of 1 kg/s with a water mole fraction of 0.1. Air flows from the bottom at a velocity of 1.7 m/s and a temperature of 393 K, causing the moisture in the soil to evaporate inside the fluidized bed. The geometry used in this project is two-dimensional, with a fluidizer height of 0.5 m and a length of 2 m.
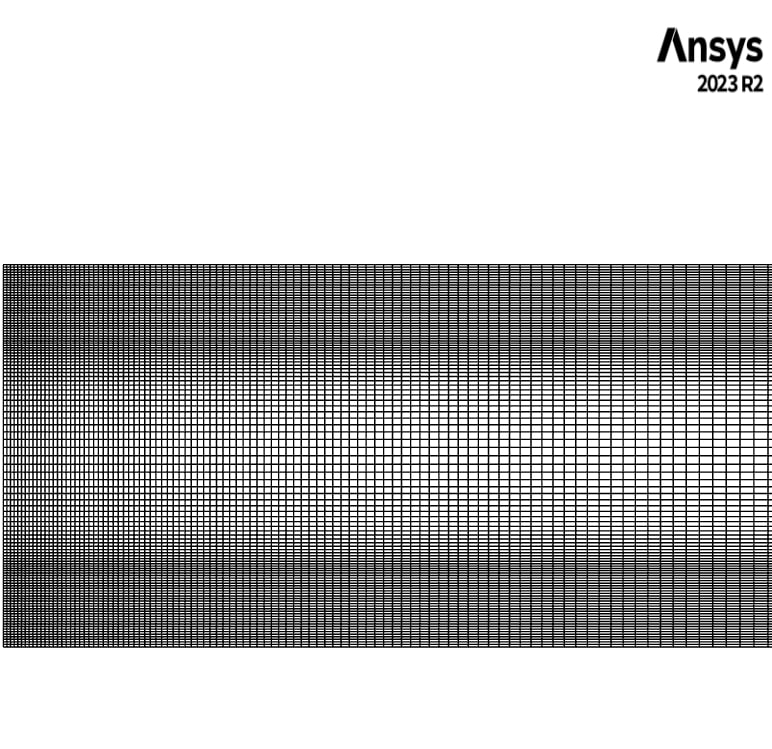
The geometry is designed in SpaceClaim® and is meshed using ANSYS Meshing®. The mesh is structured the element count is 22,000.
Methodology
This project involves solving an unsteady simulation of horizontal fluidized bed with gravity activated to account for the gravitational force on soil particles. The energy equation is also activated in this simulation.
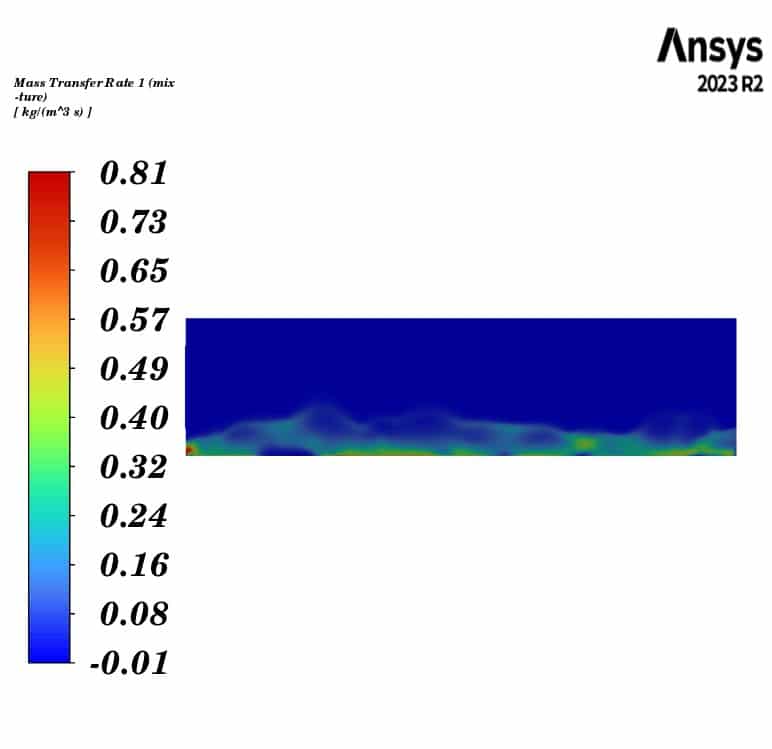
The “Eulerian” approach is selected for the multiphase flow. Each of the two defined phases contains two species defined using the species transport model. The primary phase is a gas composed of air and water vapor. The secondary phase is granular, with a particle size of 0.0018 m, and contains the species of soil and liquid water. Mass transfer between liquid water and vapor is defined using the evaporation-condensation method with the Lee model.
For modeling viscous effects, the standard k-ε model is chosen with the standard wall function due to its robustness and relatively low computational cost.
Results
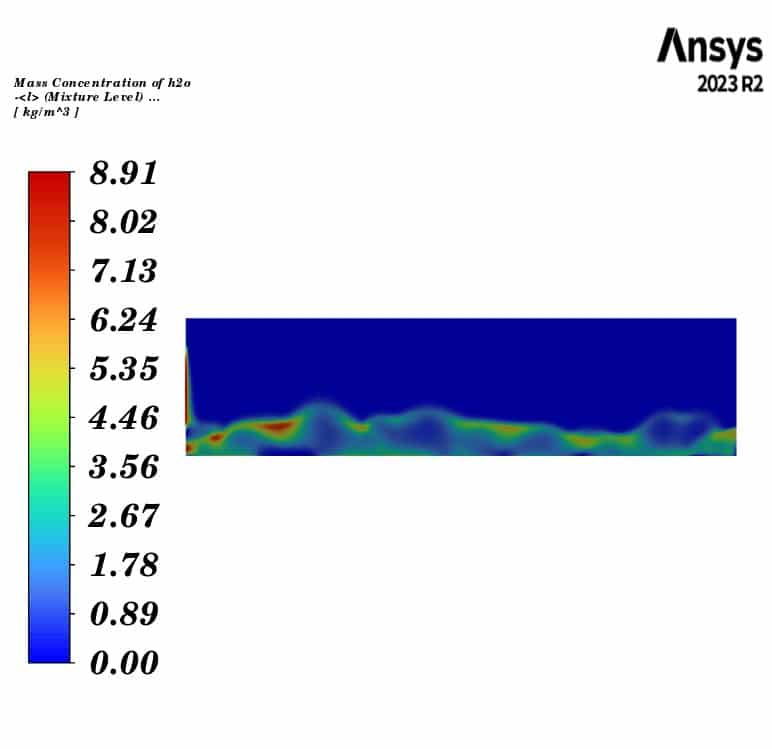
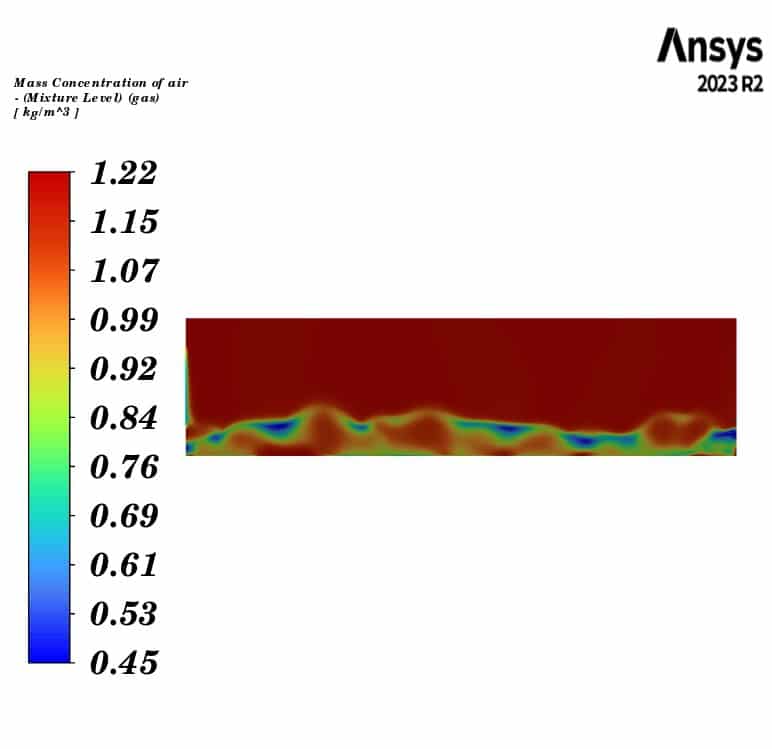
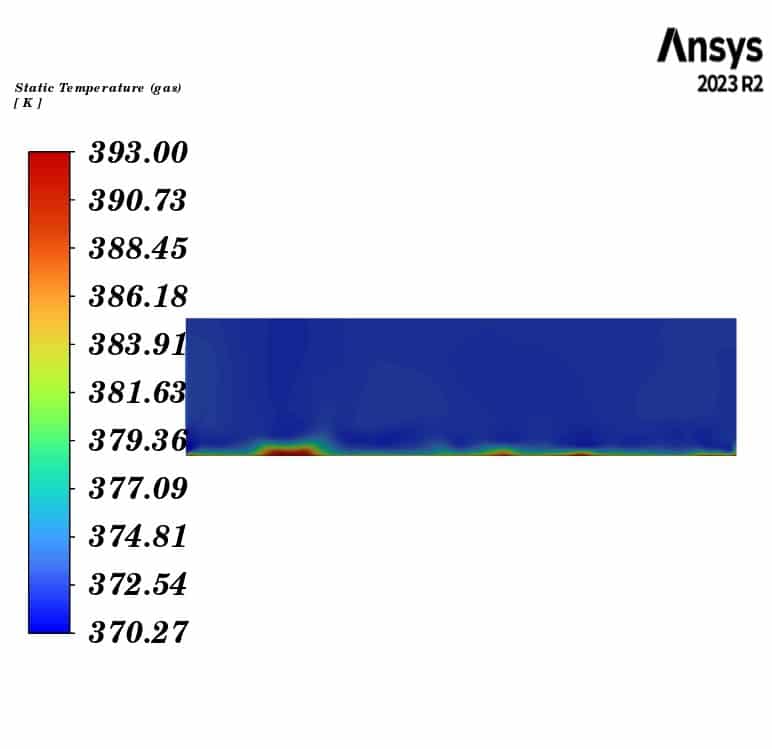
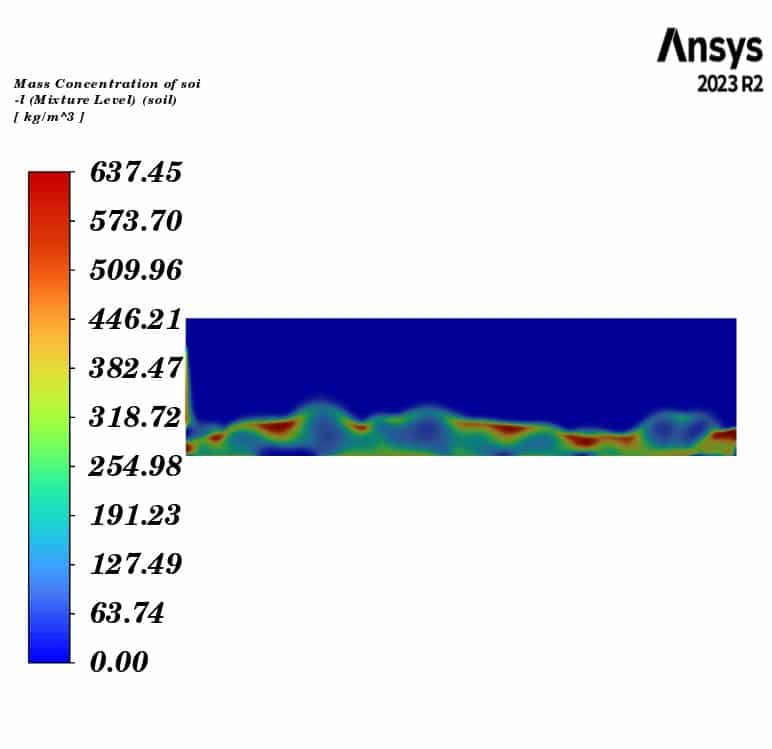
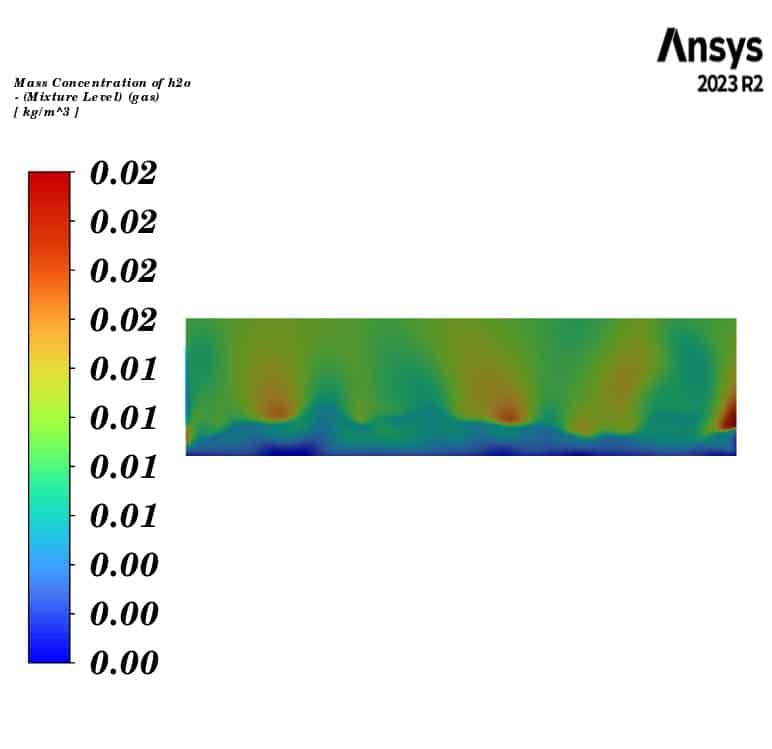
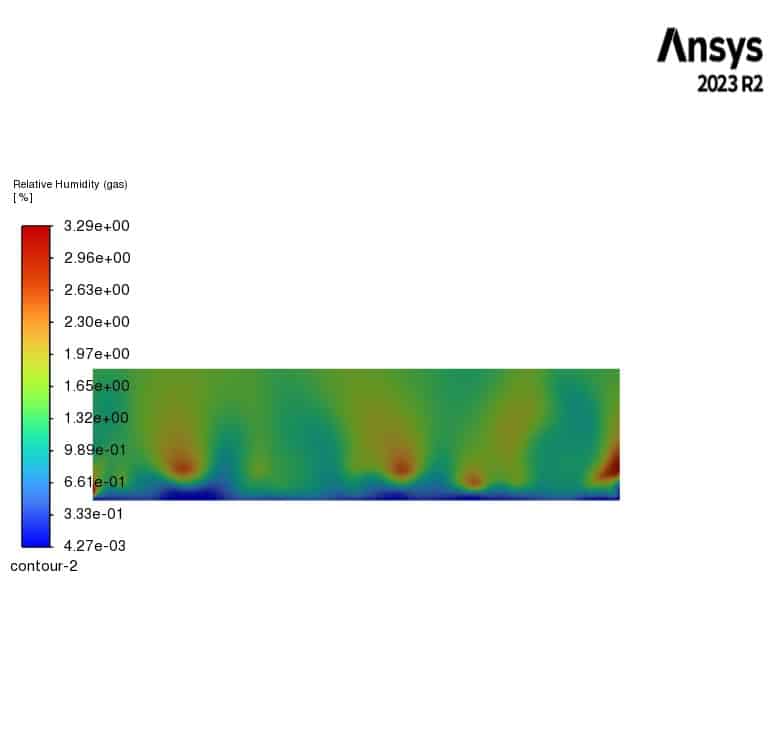
Contours of temperature and mass concentration of all species of horizontal fluidized bed are presented.
The contours illustrate the evaporation of soil moisture inside the fluidized bed. We can observe a decrease in water mass concentration and an increase in vapor concentration. Additionally, the air temperature decreases to the saturation temperature of water at the outlet, while the soil temperature remains constant throughout the fluidized bed. This indicates that the heat lost by the gas phase is consumed by the evaporation of the water.
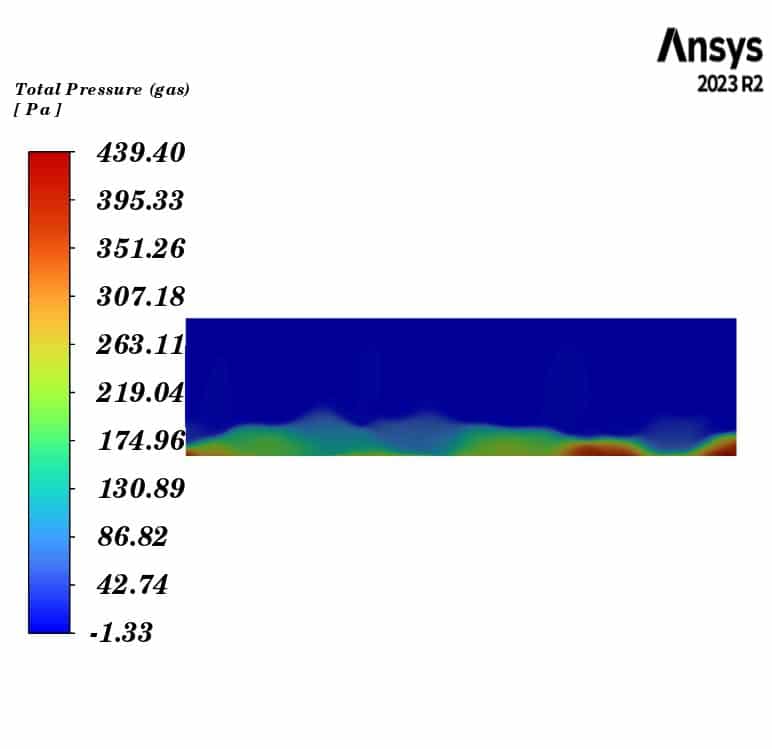
Pressure drop of gas phase in this simulation was 284.8 Pa.
Some of most important results of this simulation are list in the following table.
| Area weighted average of vapor concentration
[Kg/m3] |
mass weighted average of vapor concentration
[Kg/m3] |
Temperature
[K] |
|
| Inlet gas | 0.0017 | 0 | 393 |
| Outlet gas | 0.0108 | 1.85 e-5 | 372.4 |
| Inlet soil | 0.0058 | 7.92 | 373 |
| Outlet soil | 0.01614 | 1.91 | 373.37 |



Reviews
There are no reviews yet.