Hydro-Abrasive Erosion in Pelton Turbine CFD Simulation Tutorial
$220.00 $110.00 Student Discount
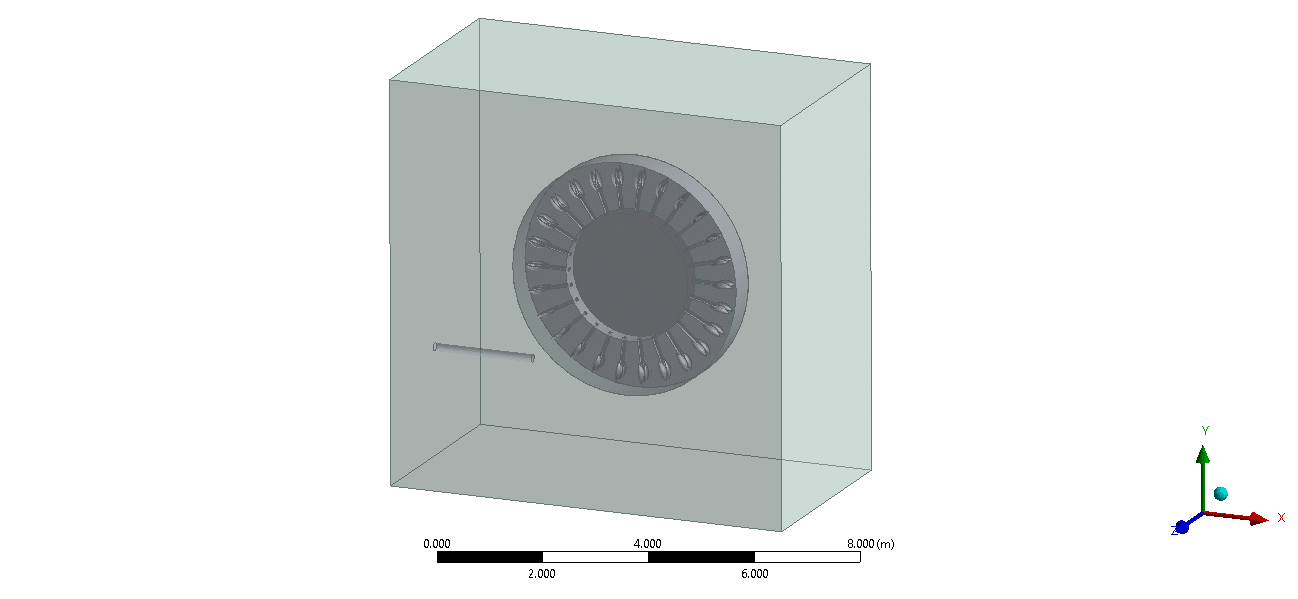
- This project numerically simulates the Hydro-Abrasive Erosion in Pelton Turbine using ANSYS Fluent software.
- The 3-D geometry is designed in Design Modeler software.
- We used ANSYS Meshing Software to generate mesh; the element number equals 6,433,121.
- The multiphase VOF model simulates the water jet.
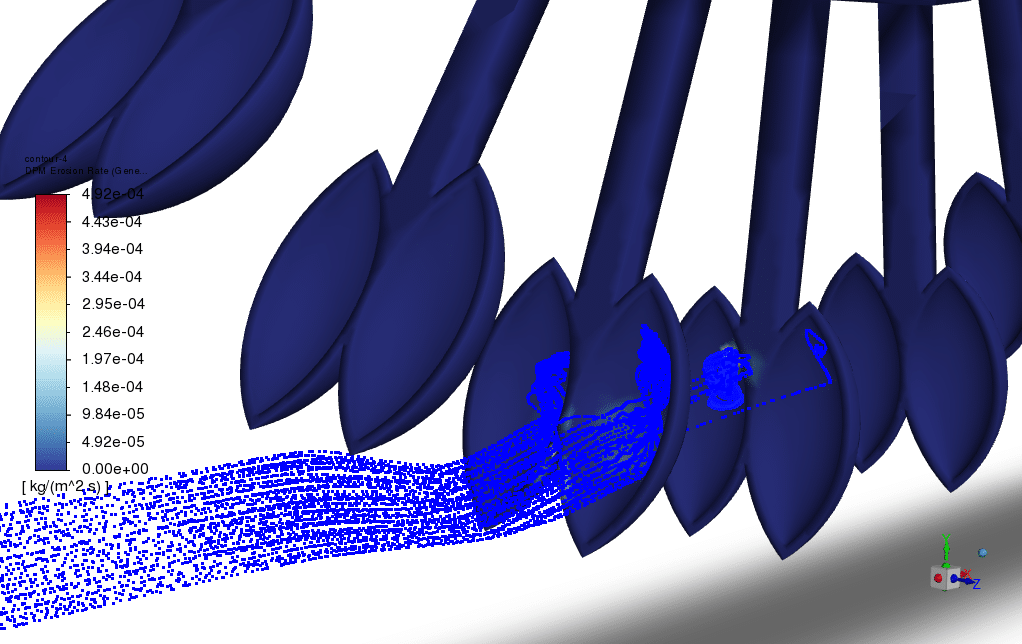
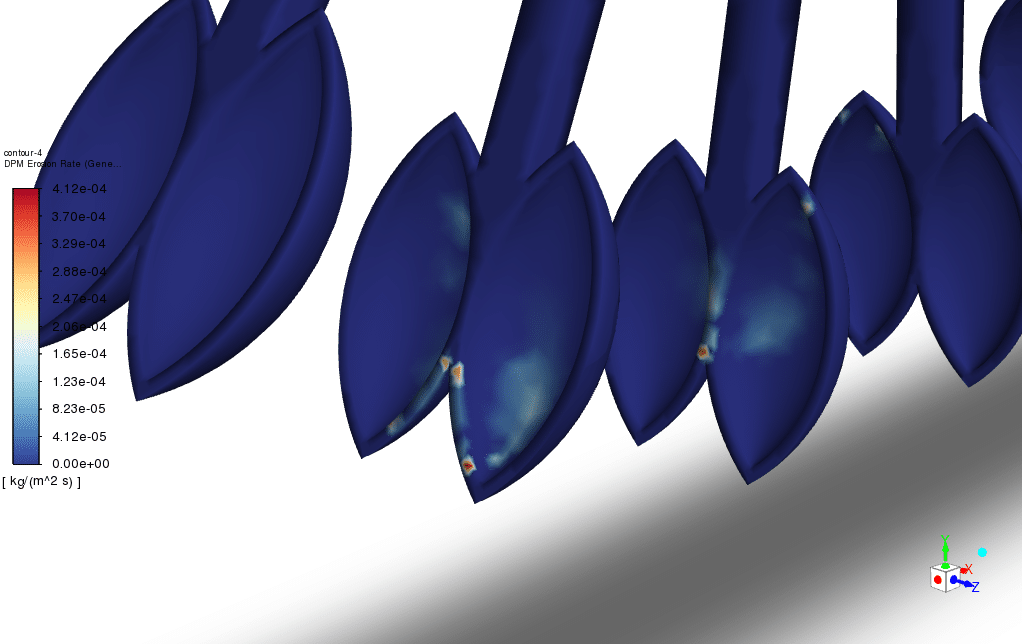
- The 2-way DPM model also enables the erosion of the solution.
- The rotational movement of the turbine is modeled using Mesh Motion Approach.
To Order Your Project or benefit from a CFD consultation, contact our experts via email (info@mr-cfd.com), online support tab, or WhatsApp at +44 7443 197273.
There are some Free Products to check our service quality.
If you want the training video in another language instead of English, ask it via info@mr-cfd.com after you buy the product.
Description
Introduction
Pelton wheel erosion is a significant concern in hydropower systems. The Pelton wheel, a key component of hydro turbines, is subjected to high-velocity water jets that can cause erosion over time. This erosion occurs primarily due to the impact of water droplets and sand particles on the wheel’s buckets or blades.
The material gradually wears away as the water repeatedly strikes the surface, reducing efficiency and potential damage. Various measures are employed to mitigate erosion, including using erosion-resistant materials, regular maintenance, and monitoring. Additionally, optimizing water flow and ensuring proper alignment can minimize erosion and extend the lifespan of Pelton wheels, ensuring efficient and sustainable hydropower generation.
The geometry used in this simulation is created with Design Modeler software, and the mesh grid is generated with ANSYS Meshing as an unstructured grid that contains 6,433,121 tetrahedral elements.
Hydro-Abrasive Erosion in Pelton Turbine Methodology
To investigate the hydro-abrasive effect, the simulation is performed with different water jet speeds, and the average erosion that occurs on the blades of the Pelton turbine is measured.
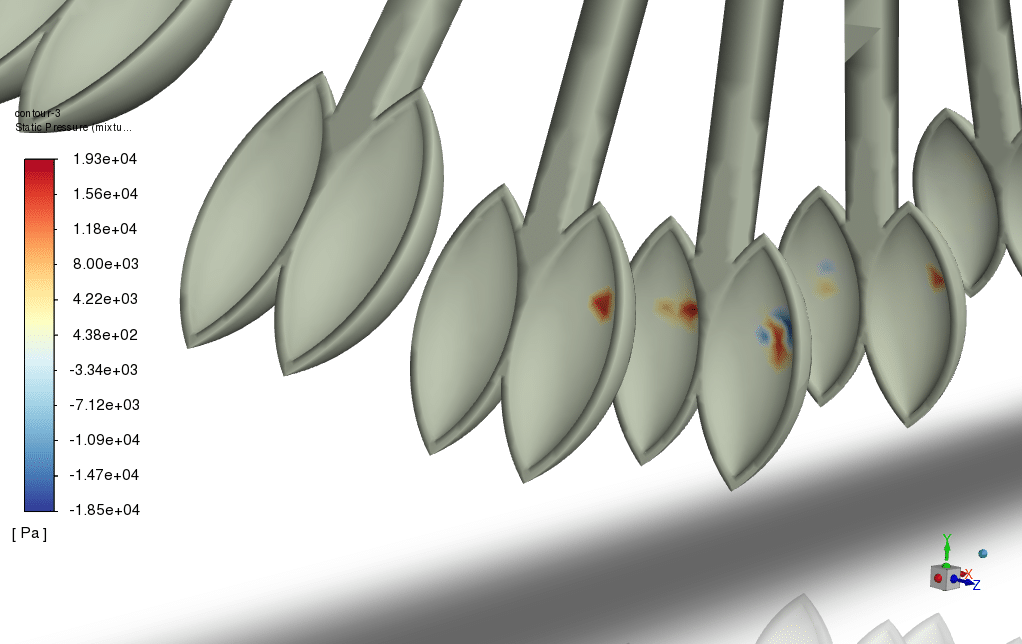
The turbulence model is set as K-Omega SST, and the multiphase VOF model simulates a water jet. The DPM model also enables to model of erosion as a 2-way DPM; the Pelton wheel motion itself is modeled using a Mesh Motion Approach.
Conclusion
After the simulation was performed, the results showed the direct impact of the high-velocity water jet on the Pelton turbine blades. create an erosion. The hydro-abrasive phenomena also depend on the varying water jet velocity. The as the velocity doubles.
The average erosion rate increases by 12%, which must be considered in the casting material process. The high erosion rate of the sand particles is a crucial factor in Pelton turbine design life expectancy.



Reviews
There are no reviews yet.