Porous CFD Simulation Training Package, Beginner, 10 Learning Products
$399.00 $199.50 Student Discount
This CFD training package, including ten practical exercises, is prepared for BEGINNER ANSYS Fluent software users interested in the Porous modules.
- Heat transfer
- Multi-phase
- Water infiltration
- Ventilation
- Biological tissue
- Fuel cell
- Perforated plate
- Porous medium
To Order Your Project or benefit from a CFD consultation, contact our experts via email (info@mr-cfd.com), online support tab, or WhatsApp at +44 7443 197273.
There are some Free Products to check our service quality.
If you want the training video in another language instead of English, ask it via info@mr-cfd.com after you buy the product.
Description
Porous CFD Simulation Training Package, ANSYS Fluent, 10 Practical Exercises
This CFD training package, including ten practical exercises, is prepared for BEGINNER ANSYS Fluent software users interested in the Porous modules. You will learn and obtain comprehensive training on how to simulate projects. The achieved knowledge will enable you to choose the most appropriate modeling approaches and methods for applications and CFD simulations.
Heat Transfer
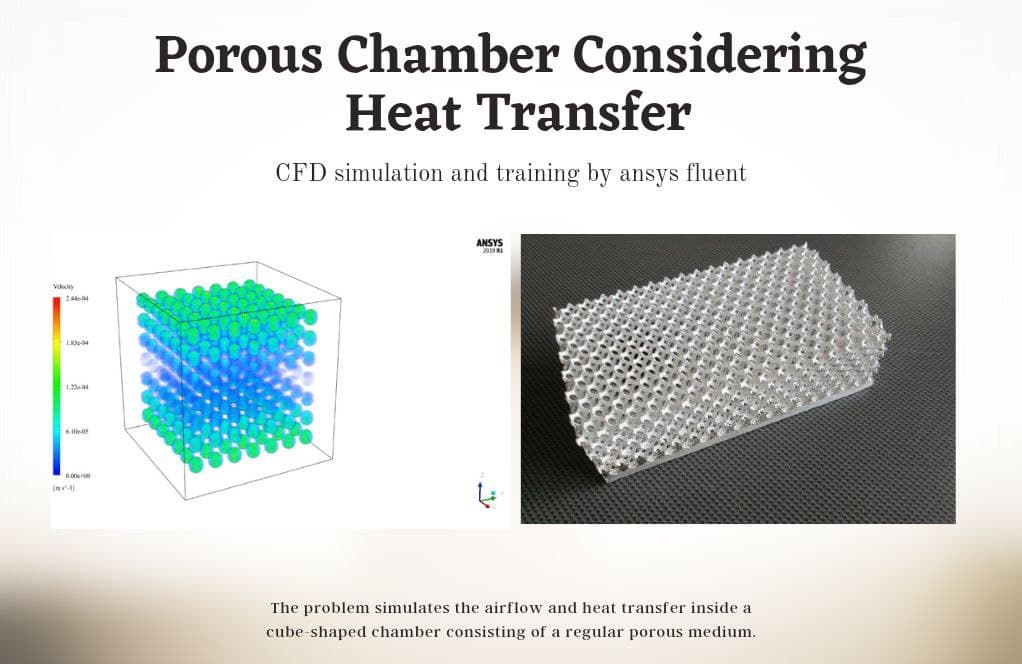
Project number 1 simulates the airflow and heat transfer inside a cube-shaped chamber with a regular real porous medium. The porous medium used in this chamber is rows and columns of several aluminum balls, the number of which is 343. The main purpose of this study is to investigate changes in air temperature inside the chamber under the influence of these items as a porous medium.
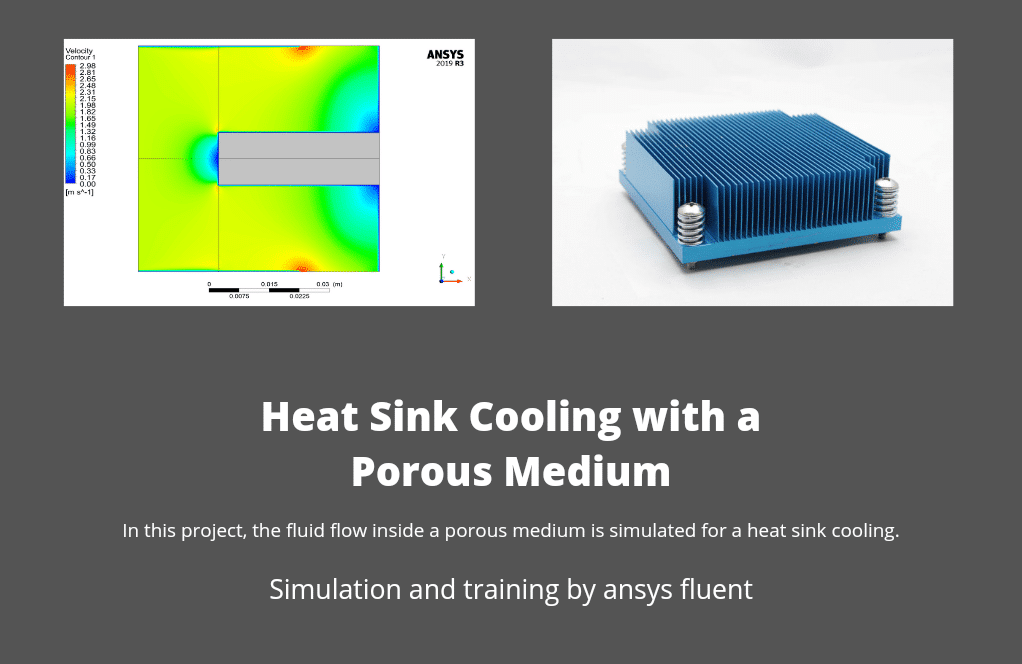
Project 2 investigates the fluid flow and heat transfer inside a porous medium. This porous medium is in contact with a heat source, and the setup acts as a heat sink. The energy model is activated, and the RNG k-epsilon model using the standard wall function is exploited for fluid flow analysis.
In project number 3, Nano-fluid flow heat transfer in a porous medium heat exchanger is simulated and analyzed. The energy model is activated. The split-Allmaras model is activated for solving turbulent flow.
Multi-phase
Project 4 simulates a three-phase flow mixture with a square cross-section within a channel. These three phases include air, water, and kerosene. In the initial state, only the airflow inside the channel is available. At the start of the simulation process, water flow enters the channel from the upper inlet section, and kerosene flow from the lower inlet section. Therefore, to simulate multi-phase flow in the present model, the VOF multiphase model has been used. Also, inside the canal, a porous environment with a porosity coefficient 0.1 is located.
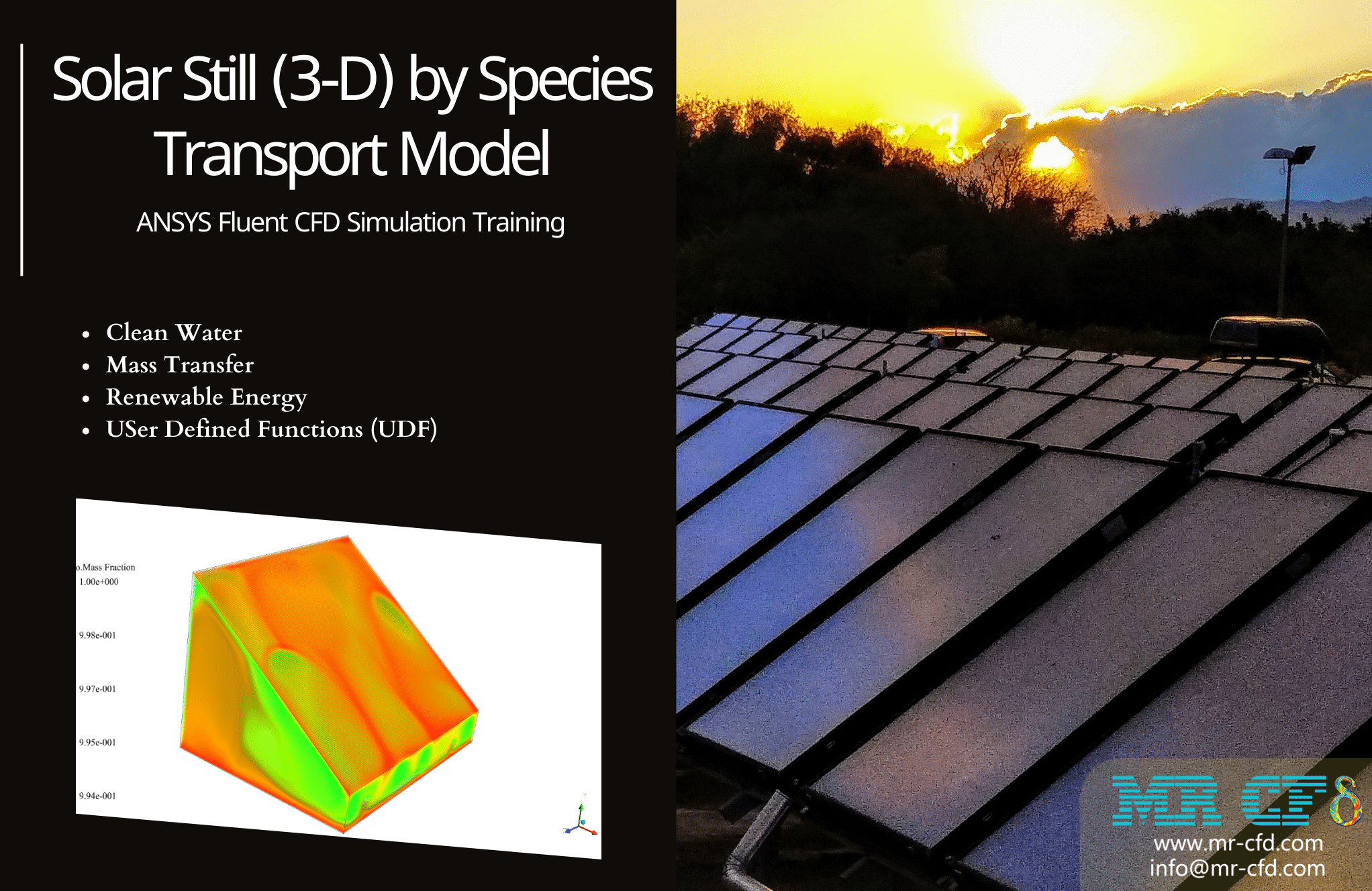
Water infiltration (Porous)
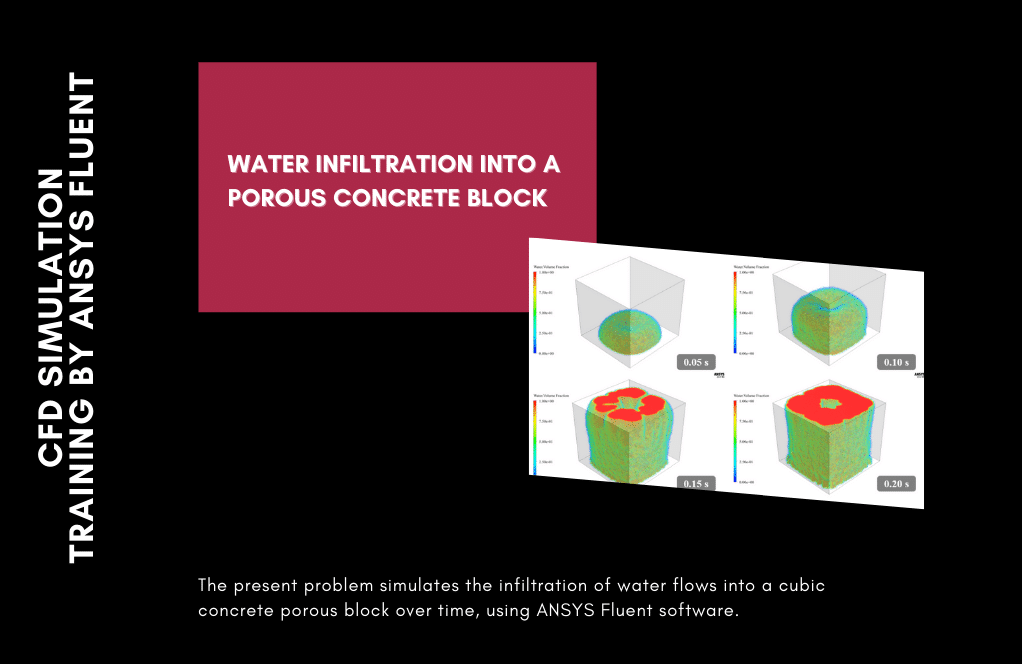
Project number 5 simulates water flow infiltration into a cubic porous medium. In this modeling, a cube block is designed as a porous medium. The water flow enters it from a circular section at the bottom of the block. The porous medium defined in the block has a porosity coefficient equal to 0.01; This means that the ratio of space to the block’s total volume equals 0.01.
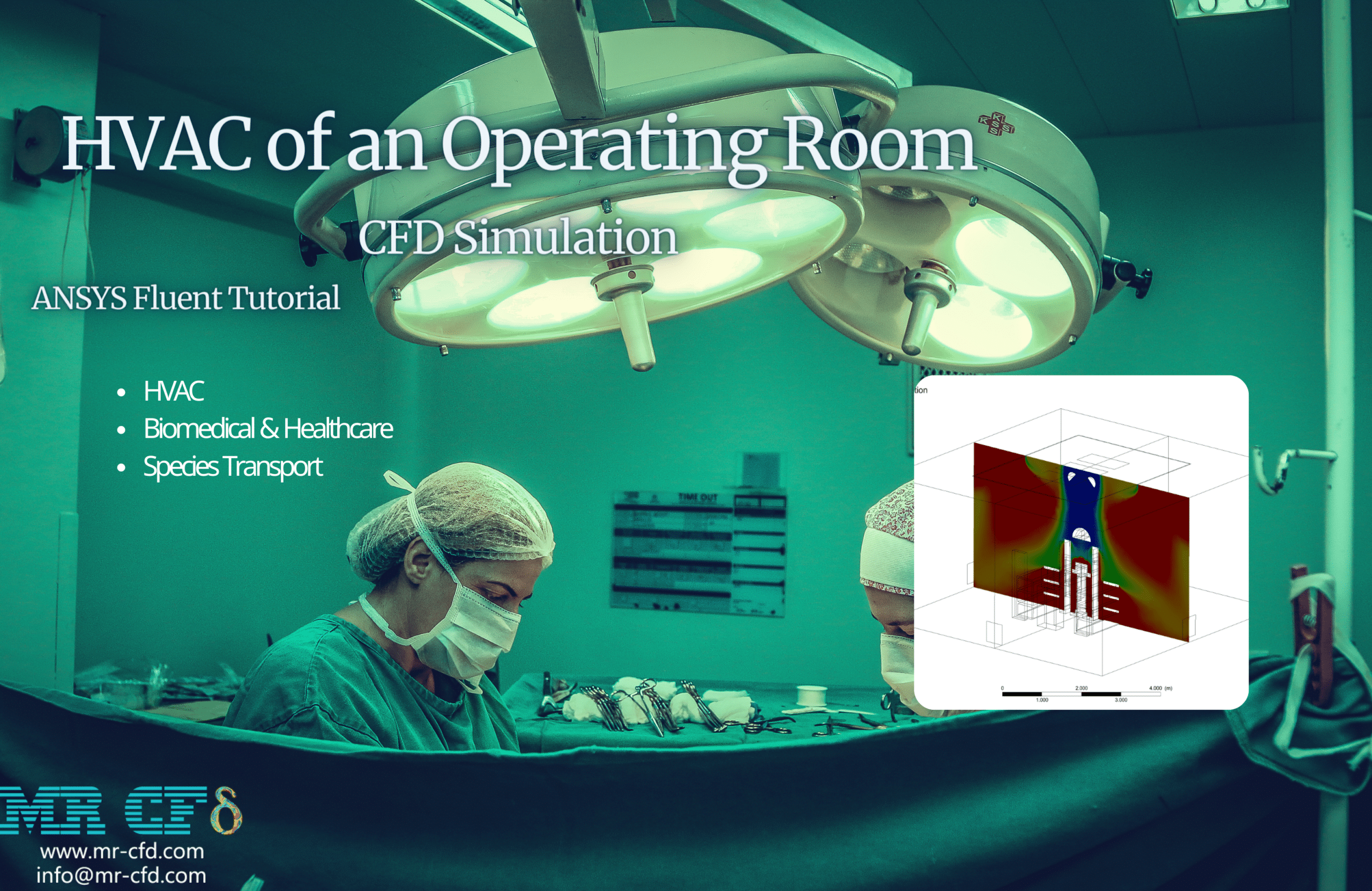
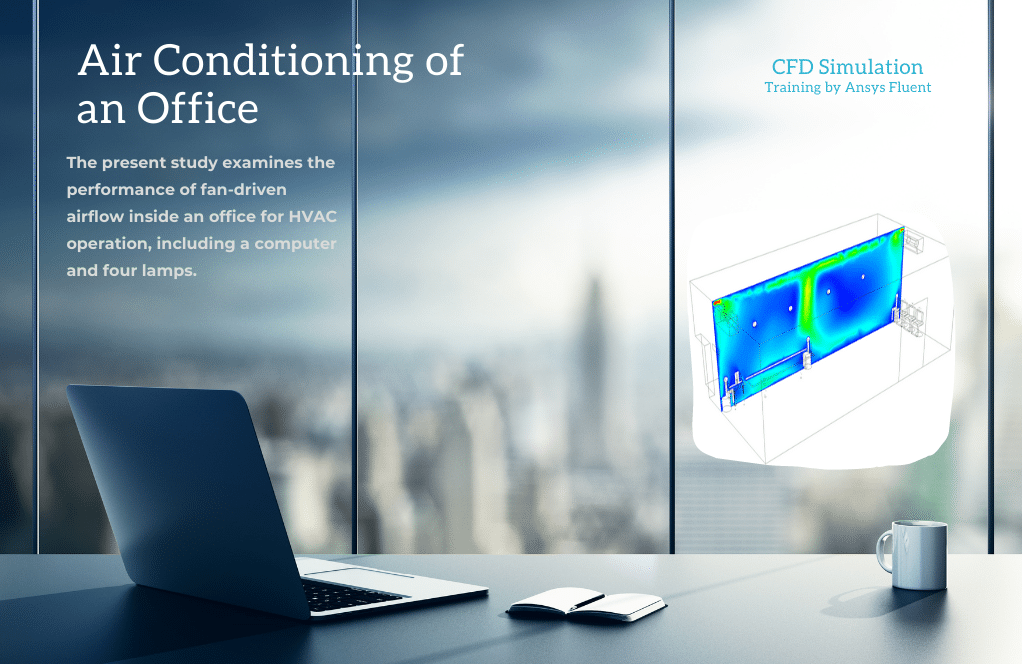
Ventilation
Project number 6 simulates the air conditioning inside a room where the transformers are located. Transformers can transfer electrical energy between two or more windings through electromagnetic induction. As a result, a variable current in the primary winding of the transformer generates a variable magnetic field, which leads to the voltage produced in the secondary winding. These transformers are considered a heat source affecting the ambient air temperature.
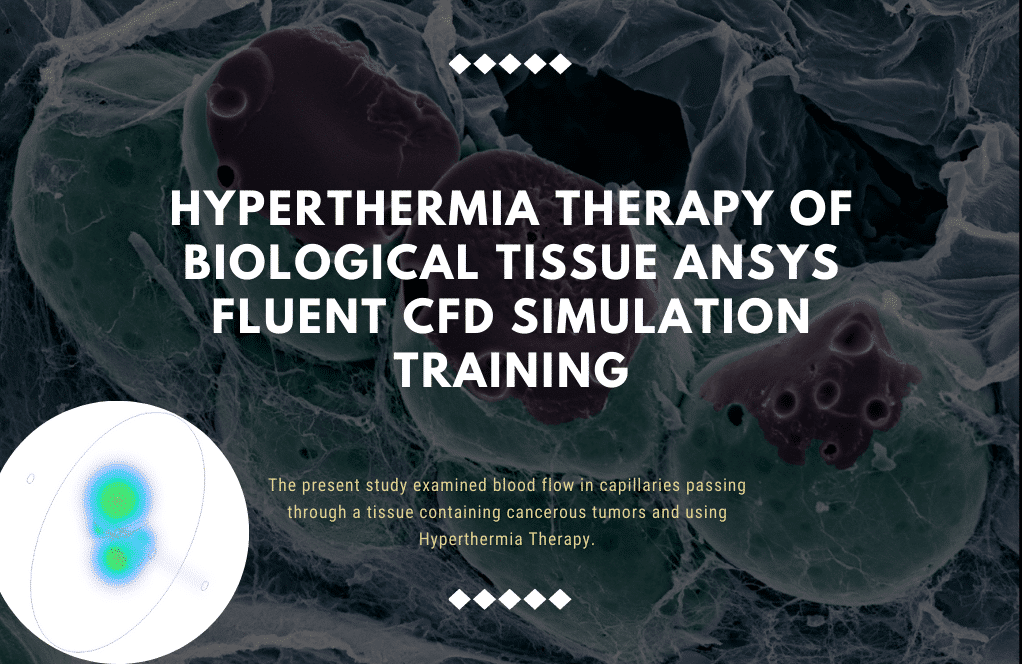
Biological Tissue
Project number 7 study examined blood flow in capillaries passing through a tissue containing cancerous tumors using Hyperthermia Therapy. For this purpose, we assume a spherical space to be an example of healthy body tissue or cell in which blood flows at a prolonged rate. There are several veins within this tissue. The vein structure of cells and tissues of the body are like bushes.
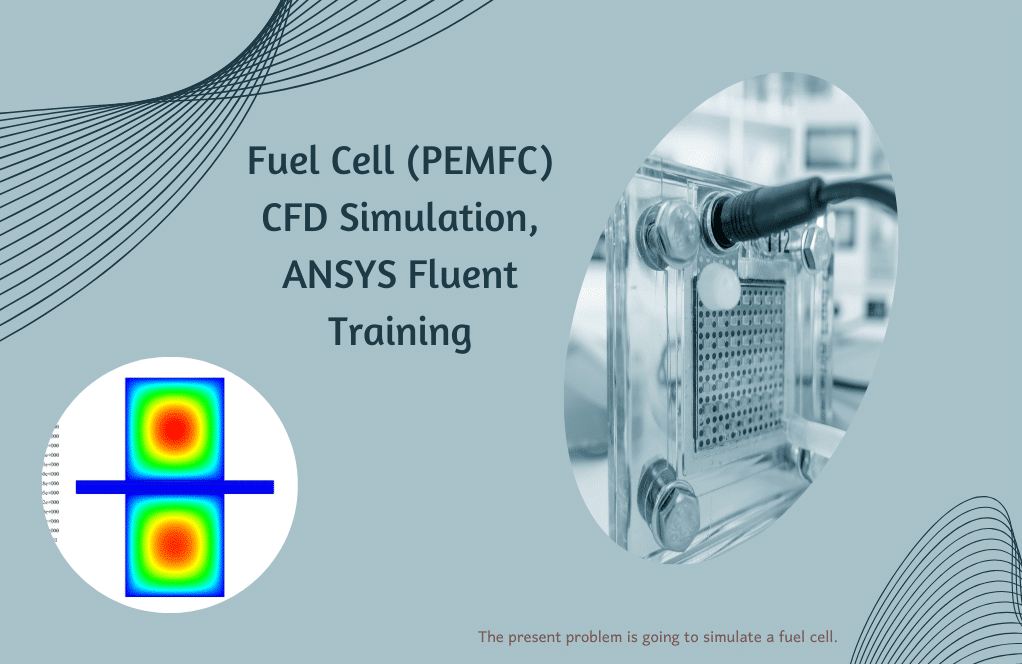
Fuel Cell (Porous)
Current collectors are solid materials with thermal energy sources and electrical potential. The flow channels carry a mixture of gaseous species, including oxygen, hydrogen, and water. The catalytic part consists of a porous medium with a porosity coefficient 0.5 and contains mass sources, thermal energy, electrical potential, proton potential, saturated water, hydrogen, oxygen, and water. Project number 8 investigates the fluid behavior and thermal conductivity of a polymer fuel cell, its effect on the mass fraction of gaseous species, and the amount of electricity produced in the cell.
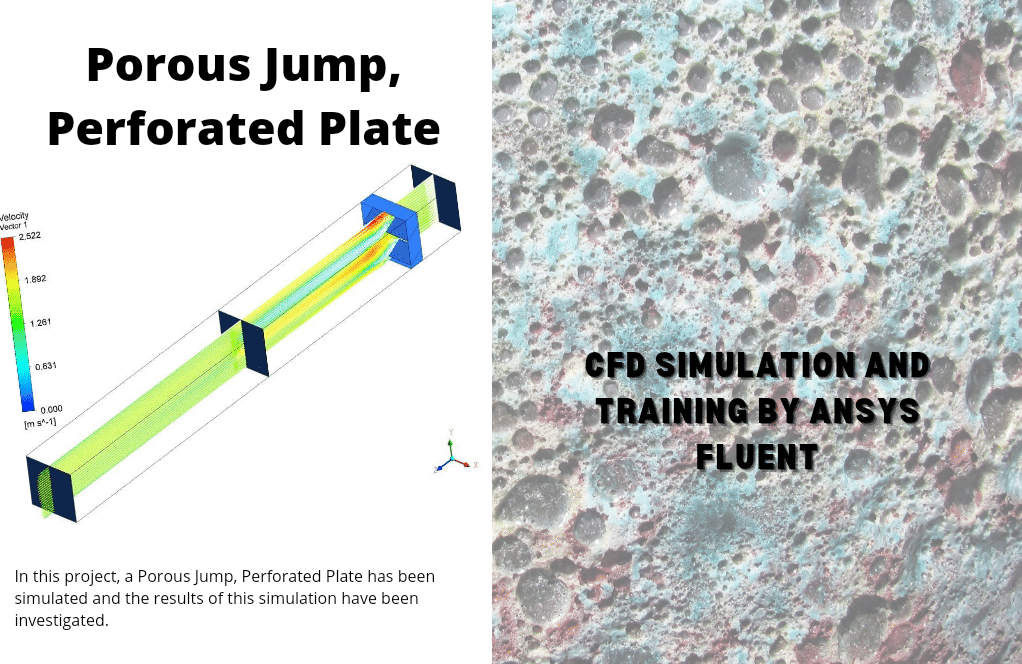
Perforated Plate
In project number 9, we studied a perforated plate. Perforated plates have patterns of holes, slots, or decorative shapes. They are widely used in industrial applications, such as filters, silencers, radiator grilles, ventilation, or separator plates. Porous jump conditions model a thin “membrane” with known velocity (pressure-drop) characteristics.
Porous Medium
In project number 10, ANSYS Fluent software investigates fluid flow through a porous medium with three different porosities. The fluid domain consists of an upstream flow domain, a porous medium domain, and a downstream flow domain. The standard k-epsilon model using the standard wall function is activated for solving fluid flow inside the computational domain.




Reviews
There are no reviews yet.