Six Blade Stirring Mixer CFD Simulation, ANSYS Fluent Training
$160.00 Student Discount
- The present problem simulates a Six Blade Stirring Mixer using ANSYS Fluent software.
- We have designed the geometry using DesignModeler software and created the mesh on this geometry using ANSYS Meshing software. The mesh type is unstructured with 5,447,852 cells.
- The Mixture multiphase model has been used to simulate the present model.
- The Multiple Reference Frames (MRF) model is used to simulate the motion of impeller.
- The solution is steady, and the k-Ꜫ model is chosen to simulate the turbulence of the flow.
To Order Your Project or benefit from a CFD consultation, contact our experts via email (info@mr-cfd.com), online support tab, or WhatsApp at +44 7443 197273.
There are some Free Products to check our service quality.
If you want the training video in another language instead of English, ask it via info@mr-cfd.com after you buy the product.
Description
Introduction
This product introduces a six blade Stirring mixer using carried out using ANSYS Fluent software. Mixing procedures are crucial in pharmaceuticals and food processing. Mixing equipment performance affects product quality, energy utilization, and process time. CFD is being used to design and analyze mixing equipment. It allows engineers to design the greatest mixers before building them. Learn how to utilize ANSYS Fluent software, the top choice for fluid dynamics modelling, to simulate a six blade Stirring mixer using CFD.
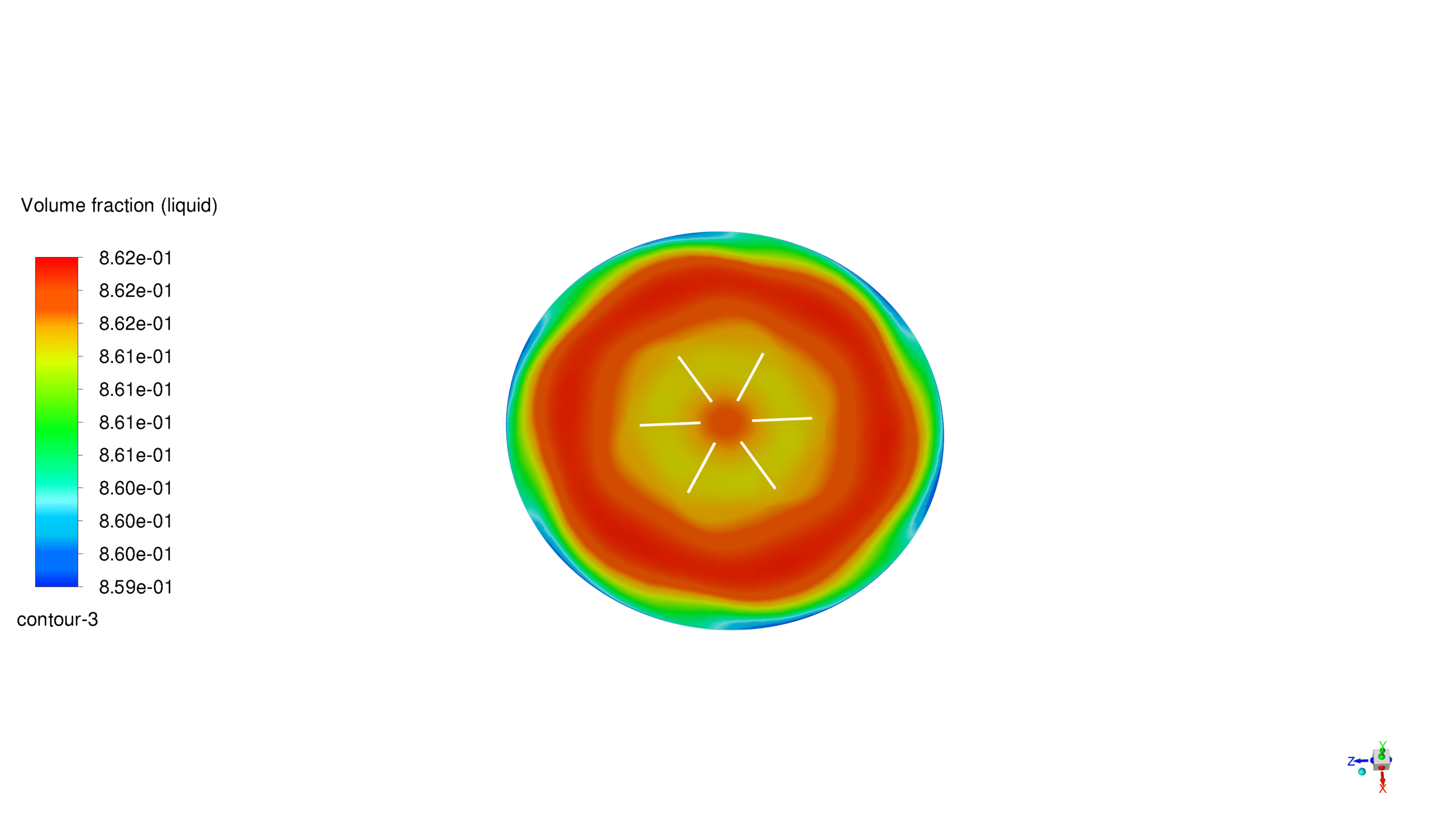
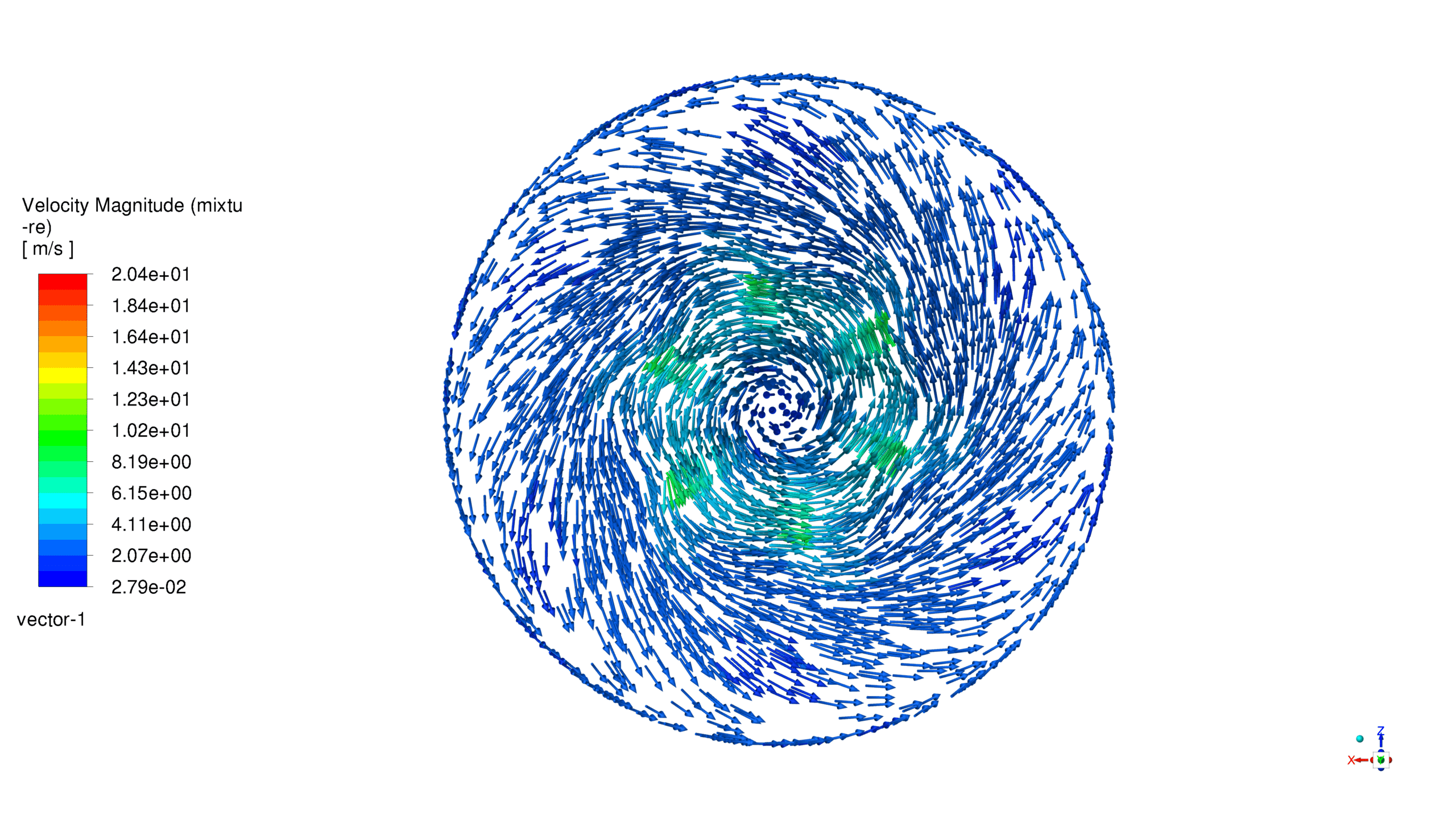
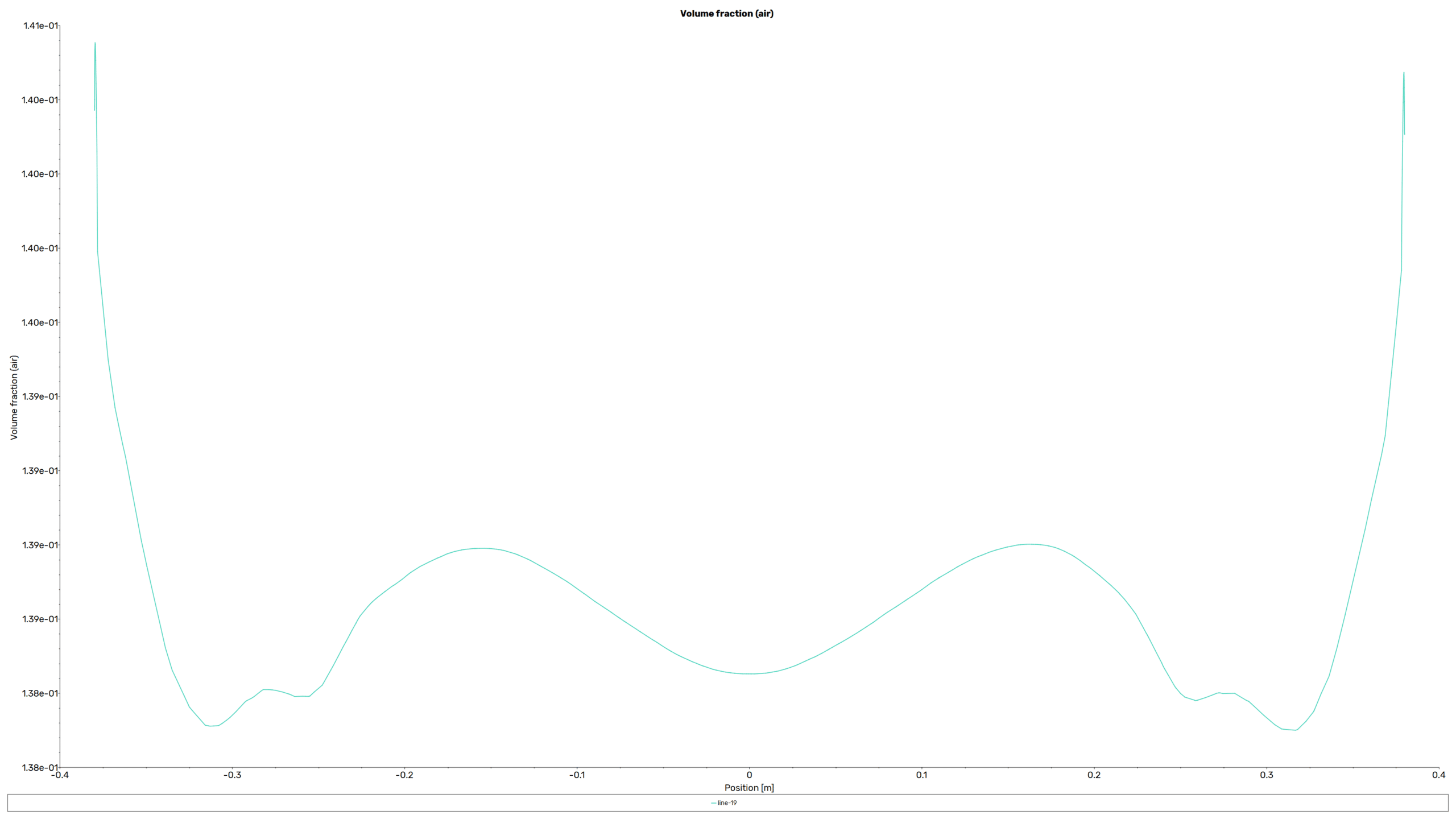
The mixer has six flat wings that rotate swiftly inside a cylindrical tank. This simulation examines the fluid dynamics of a water-air mixture to understand how the liquid phase is dispersed in the tank. The lesson shows how to replicate mixer blade rotation using the Multiple Reference Frame (MRF) method without shifting mesh techniques, which are more computationally costly. The Mixture multiphase model shows how water and air interact, helping us precisely measure water’s volume share during mixing.
The geometry of the solution was created with the ANSYS suite program Design Modeler, ensuring the geometry faithfully reflected the real model required close attention to detail.
After the design stage, an unstructured mesh was generated using the ANSYS Meshing. Higher precision in regions with anticipated volume fraction and pressure gradients was the reason a high-quality mesh was created.
Methodology
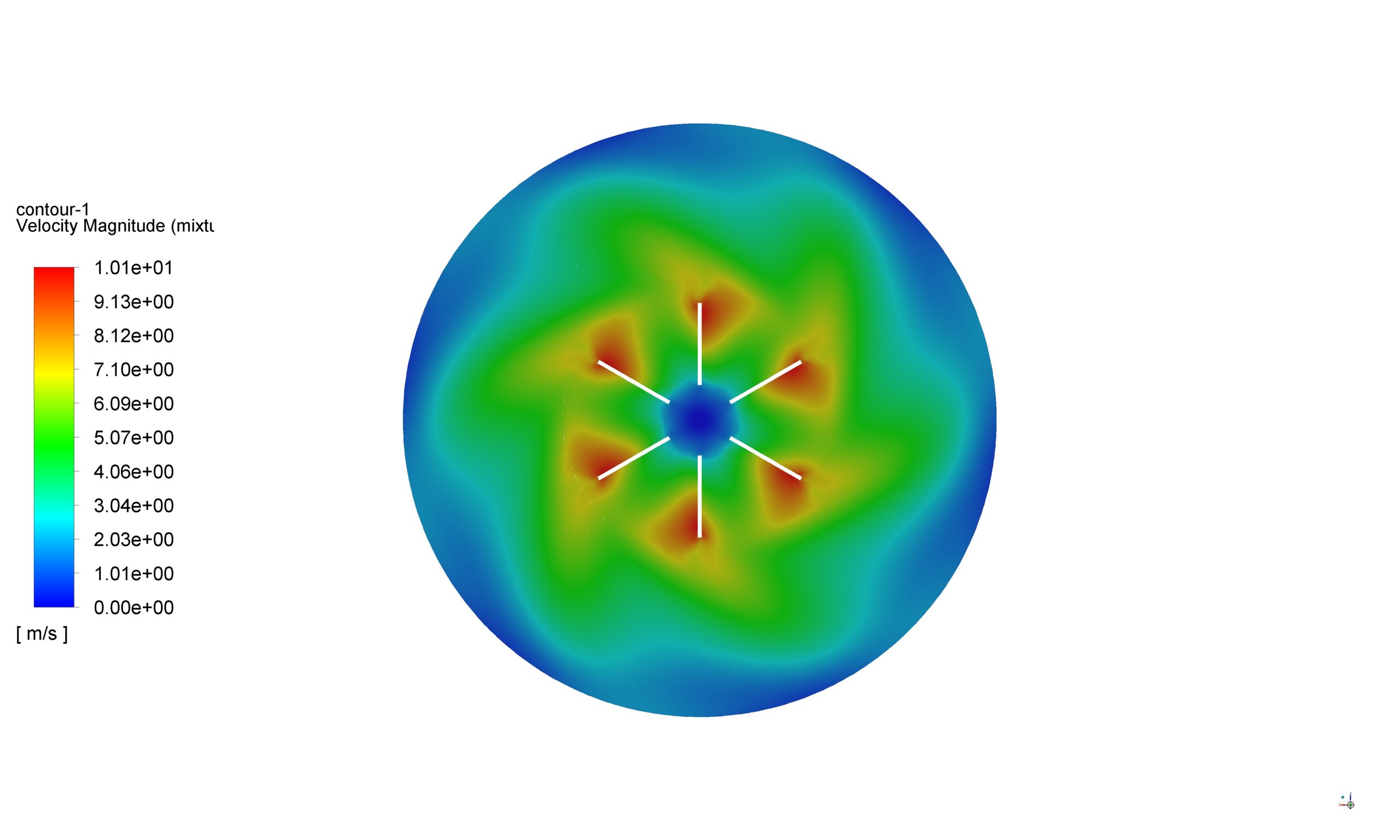
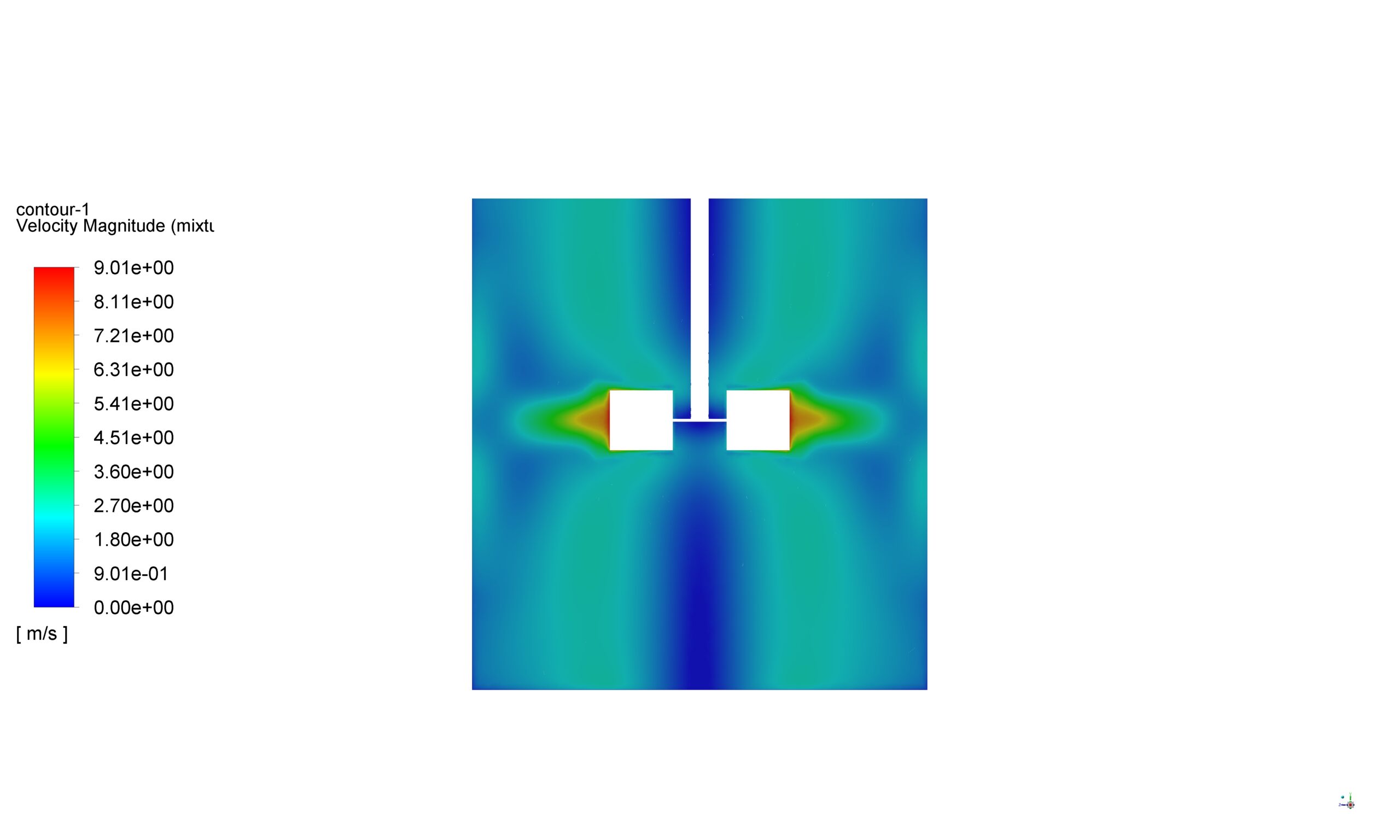
To simulate the rotational motion of the mixer, the MRF method is employed. This approach treats the rotating and stationary regions of the computational domain separately. The rotating zone, encompassing the impeller blades, is assigned a rotational speed of 550 rad/sec, while the stationary zone represents the tank. The interface between these zones is defined to allow for the transfer of flow information.
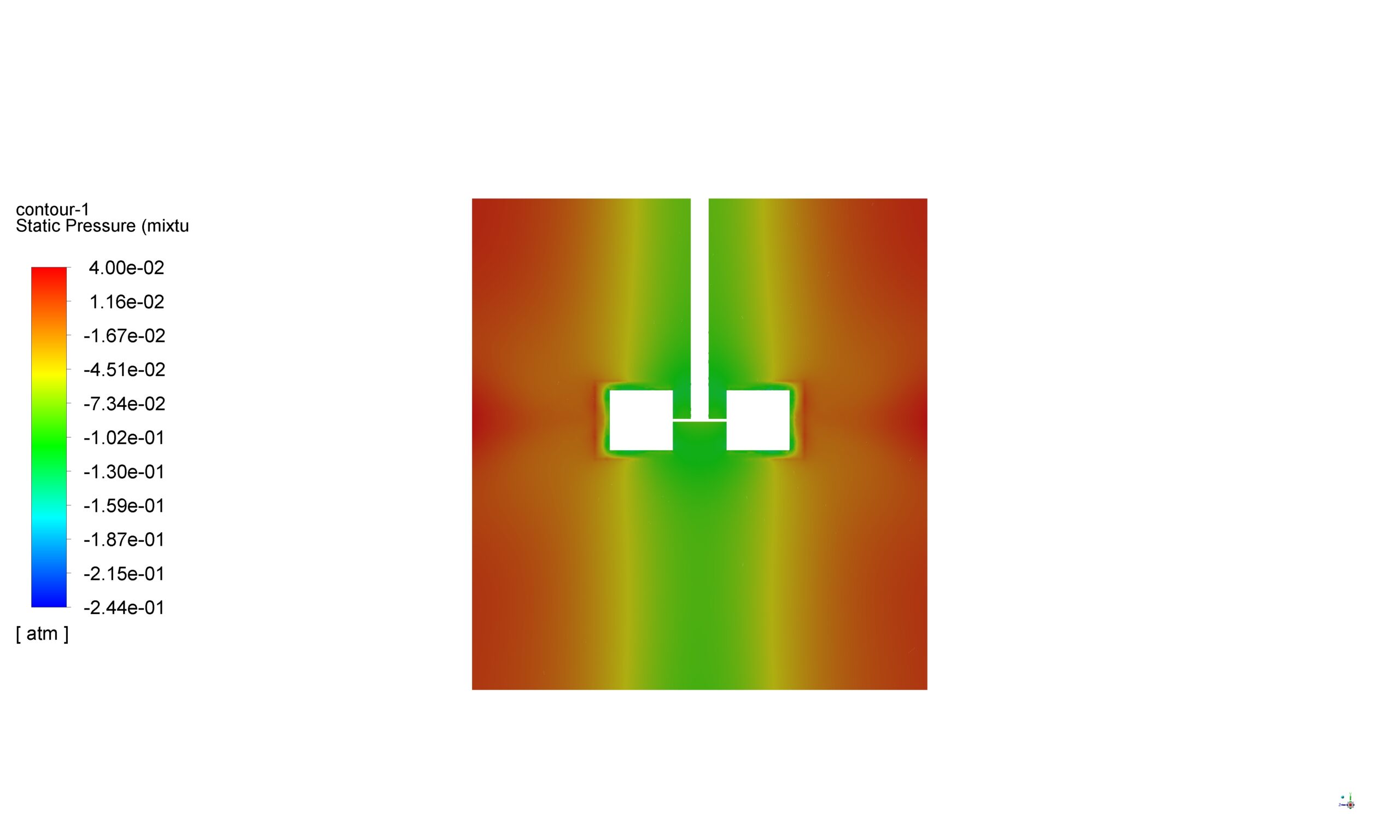
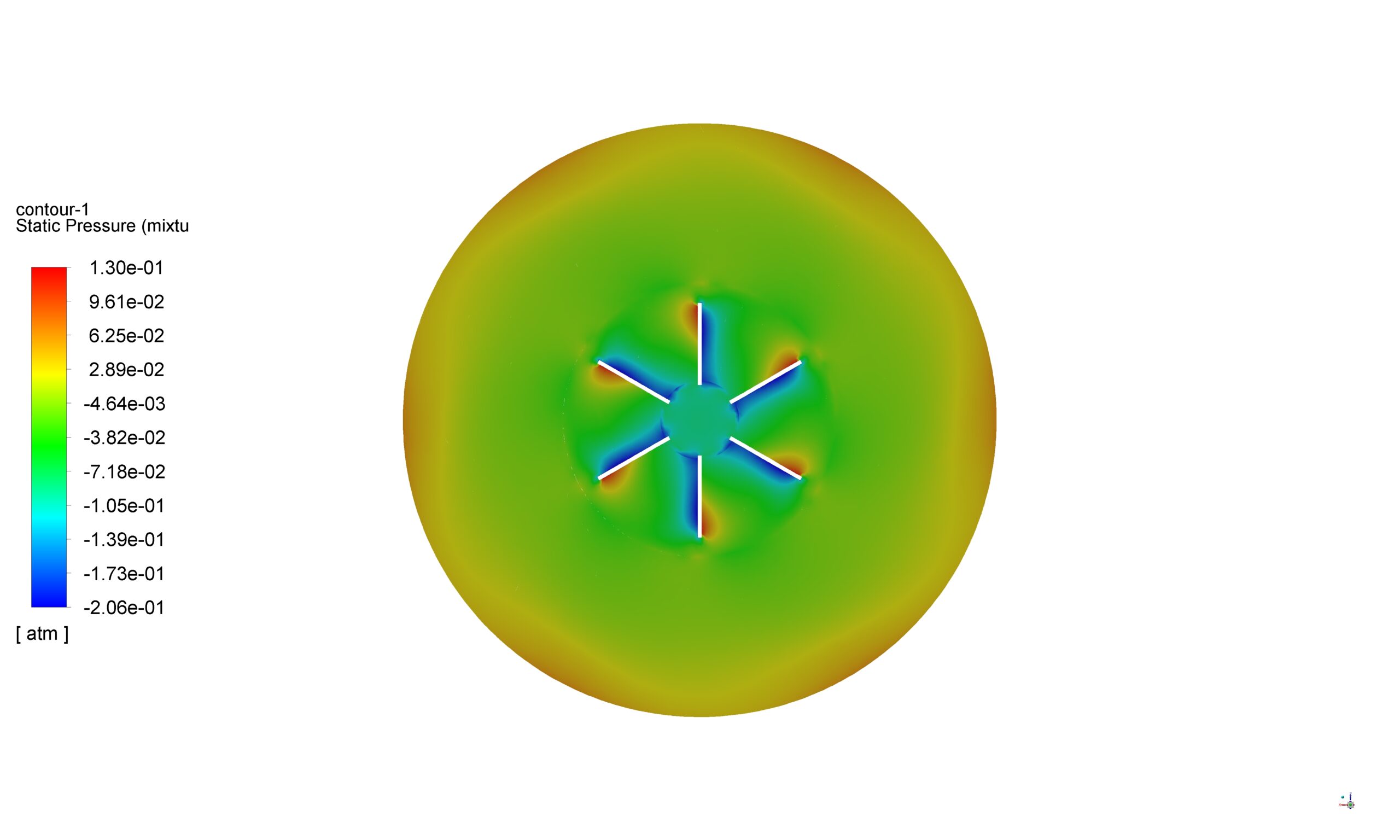
The Mixture multiphase model is selected to handle the water-air phases within the tank. This model treats the multiphase flow as a pseudo-homogeneous mixture, with each phase sharing a common pressure field. The volume fraction of the water liquid phase is tracked using an implicit solution method, ensuring numerical stability even at high rotational speeds.
The simulation is initialized and run until a steady-state solution is achieved, ensuring convergence of all relevant physical quantities.
Conclusion
The simulation of the six-blade mixer in ANSYS Fluent provides valuable insights into the mixing dynamics of a water-air system. The MRF method proves to be an efficient way to model the rotational movement of the mixer blades, reducing computational costs while maintaining accuracy. The Mixture multiphase model successfully captures the distribution of the water volume fraction, highlighting areas of effective mixing and potential dead zones within the tank.
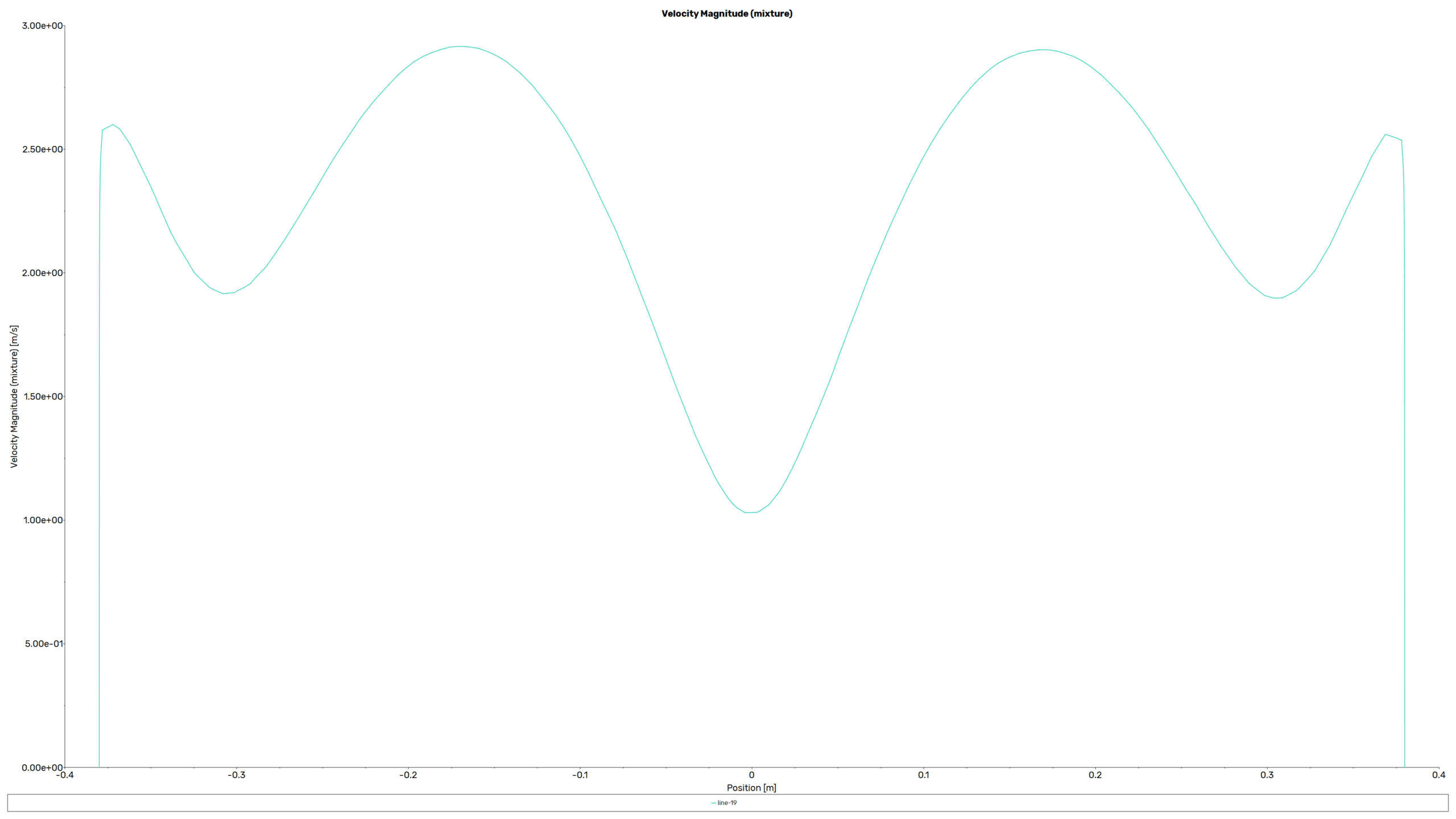
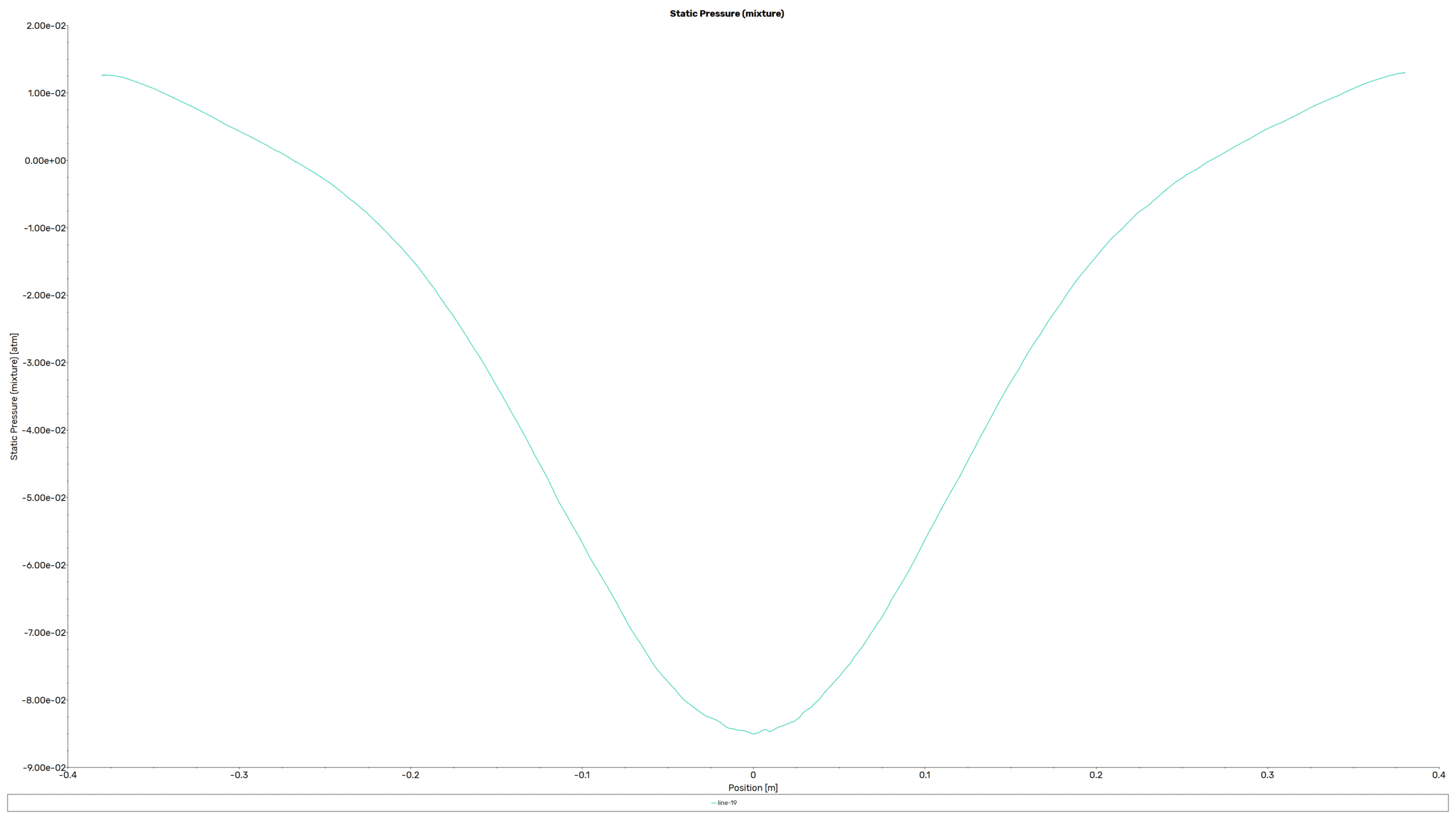
Contours, vectors and plots of different parameters, such as velocity, pressure, and volume fraction of liquid and air all around the domain are visible via high-quality figures exported from the software.
With CFD tools like ANSYS Fluent, the ability to predict and improve mixer performance becomes more accessible, paving the way for innovative design solutions and process optimizations.


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.