Temperature Rise inside the Building after Fire of leaking methane gas
$160.00 $80.00 Student Discount
- In this project, fire of a fuel tank caused by fuel leakage is modeled using ANSYS Fluent.
- The geometry was created in SpaceClaim, and a mesh consisting of 1,262,049 elements was generated using ANSYS Meshing.
- The effect of blowing wind on the temperature of the room 10m away from this tank is investigated.
To Order Your Project or benefit from a CFD consultation, contact our experts via email (info@mr-cfd.com), online support tab, or WhatsApp at +44 7443 197273.
There are some Free Products to check our service quality.
If you want the training video in another language instead of English, ask it via info@mr-cfd.com after you buy the product.
Description
Description
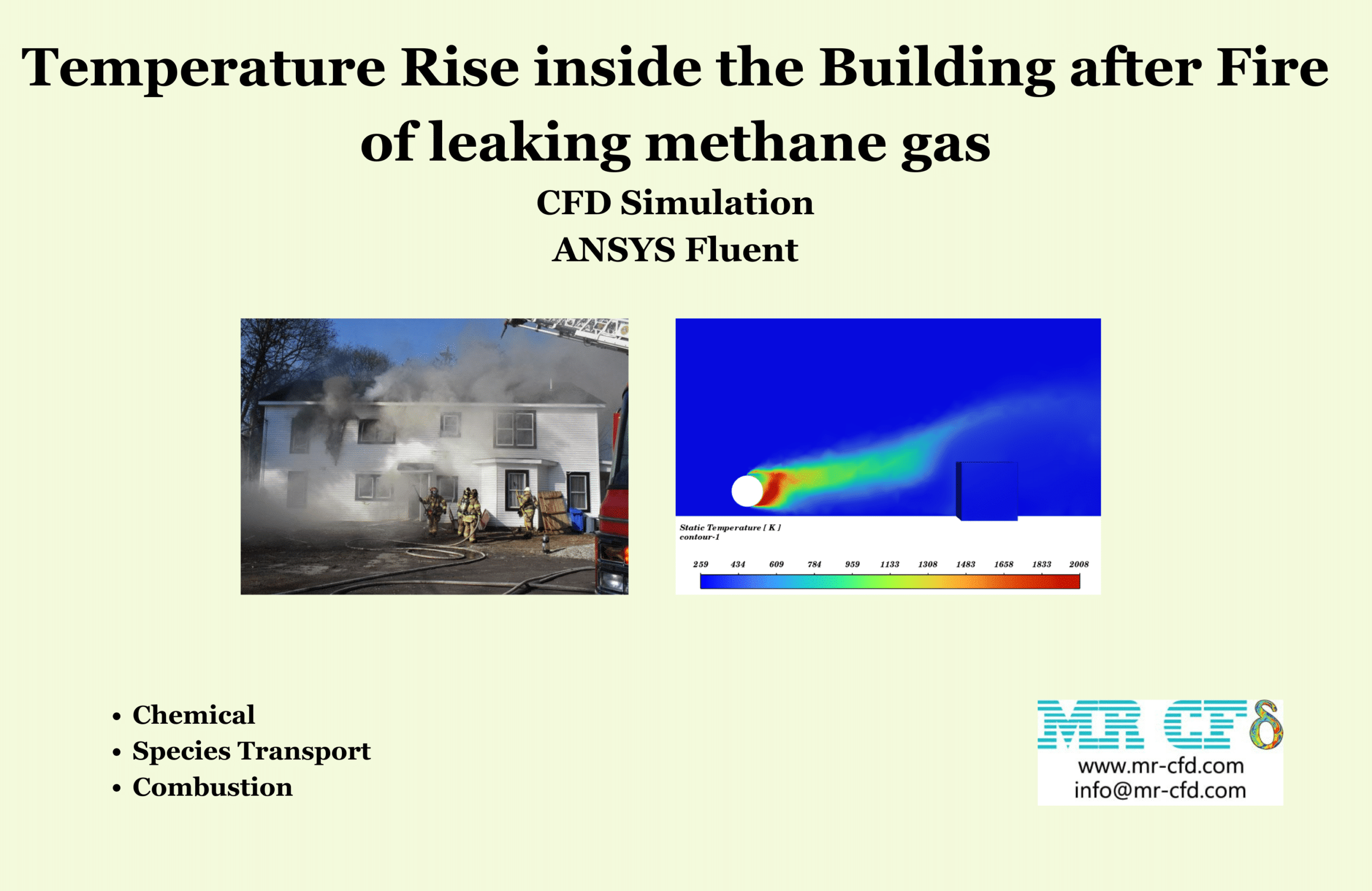
In this project, the fire of a methane fuel source due to fuel leakage is modeled. The fuel source is located at a distance of 10 meters from the engineering room, and the fuel flow from the source is 0.5 kg/s. Simulation is done in 2 cases of calm weather and with 10 m/s wind.
The geometry was designed in SpaceClaim® and meshed using ANSYS Meshing®. The mesh is unstructured and the total element count is 38,231,624.
Methodology
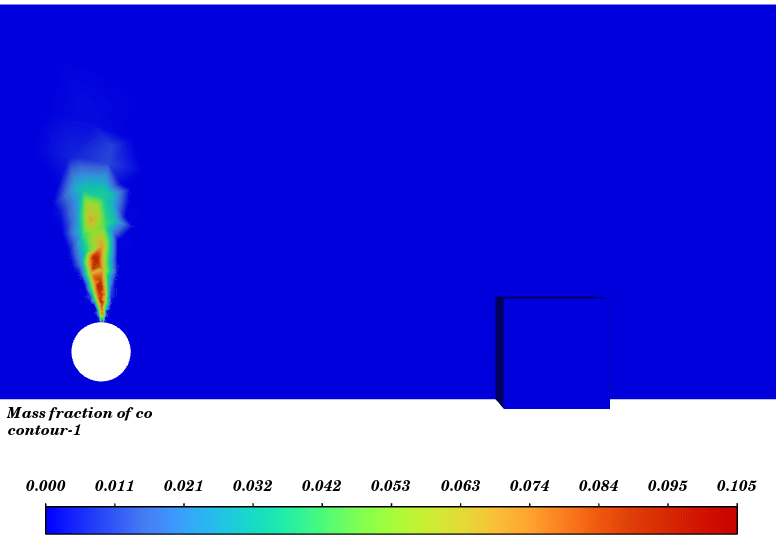
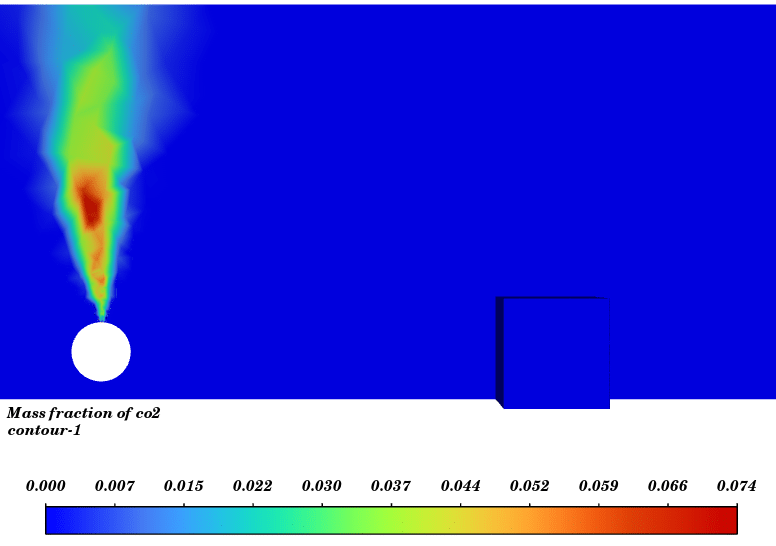
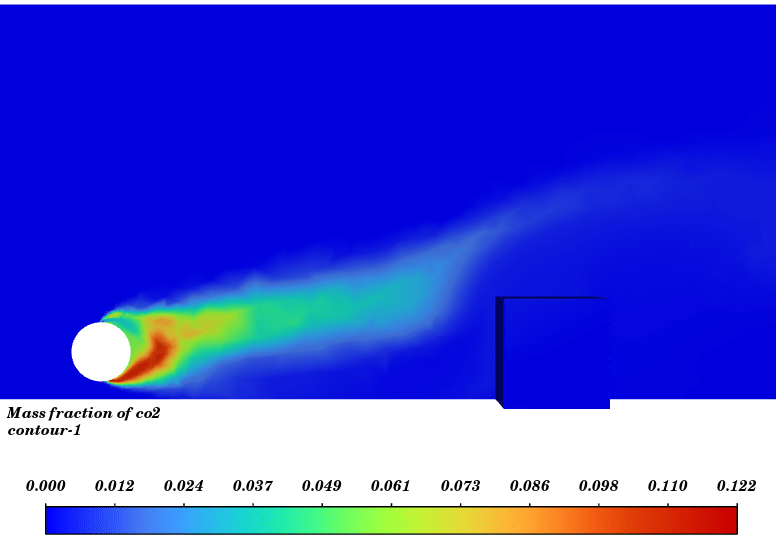
In this simulation, Energy equation is activated the turbulence effect is modeled with the k-ε standard model. For modeling the buoyancy, gravity is activated and the density model of mixture is defined as ideal gas. For the reaction modeling we used non-premixed model with CH4 fuel and air oxidizer. Number of species is defined 8 so, CH4, O2, N2, OH, CO, CO2, H2O and H2 are added.
Results
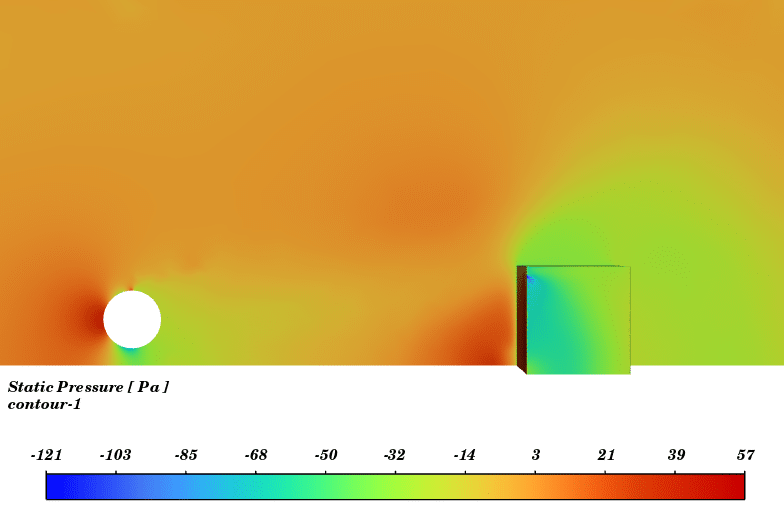
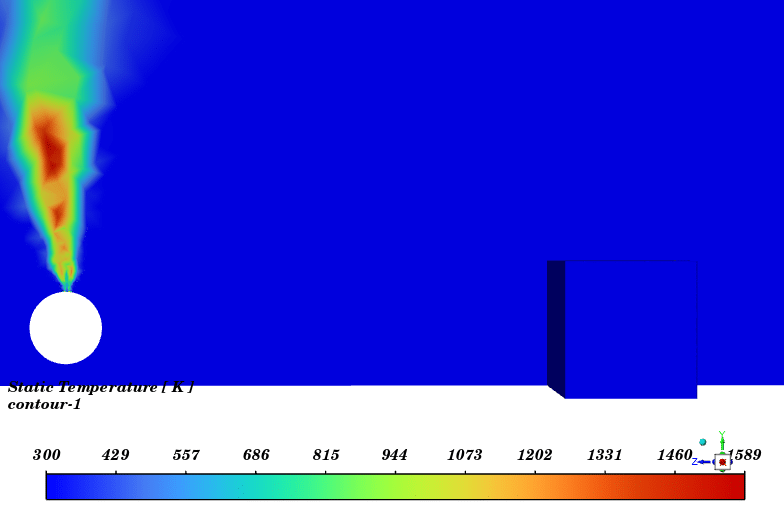
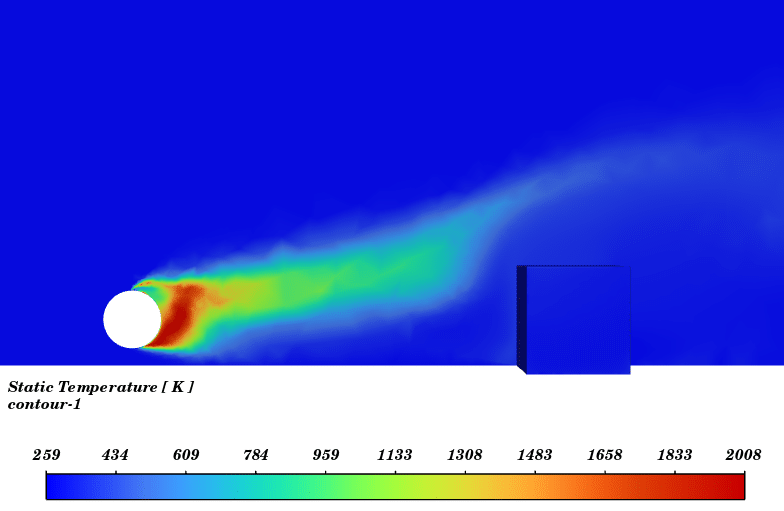
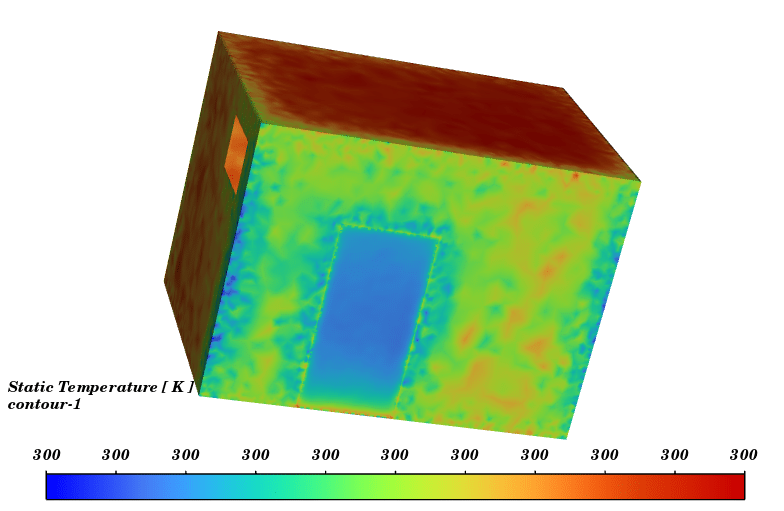
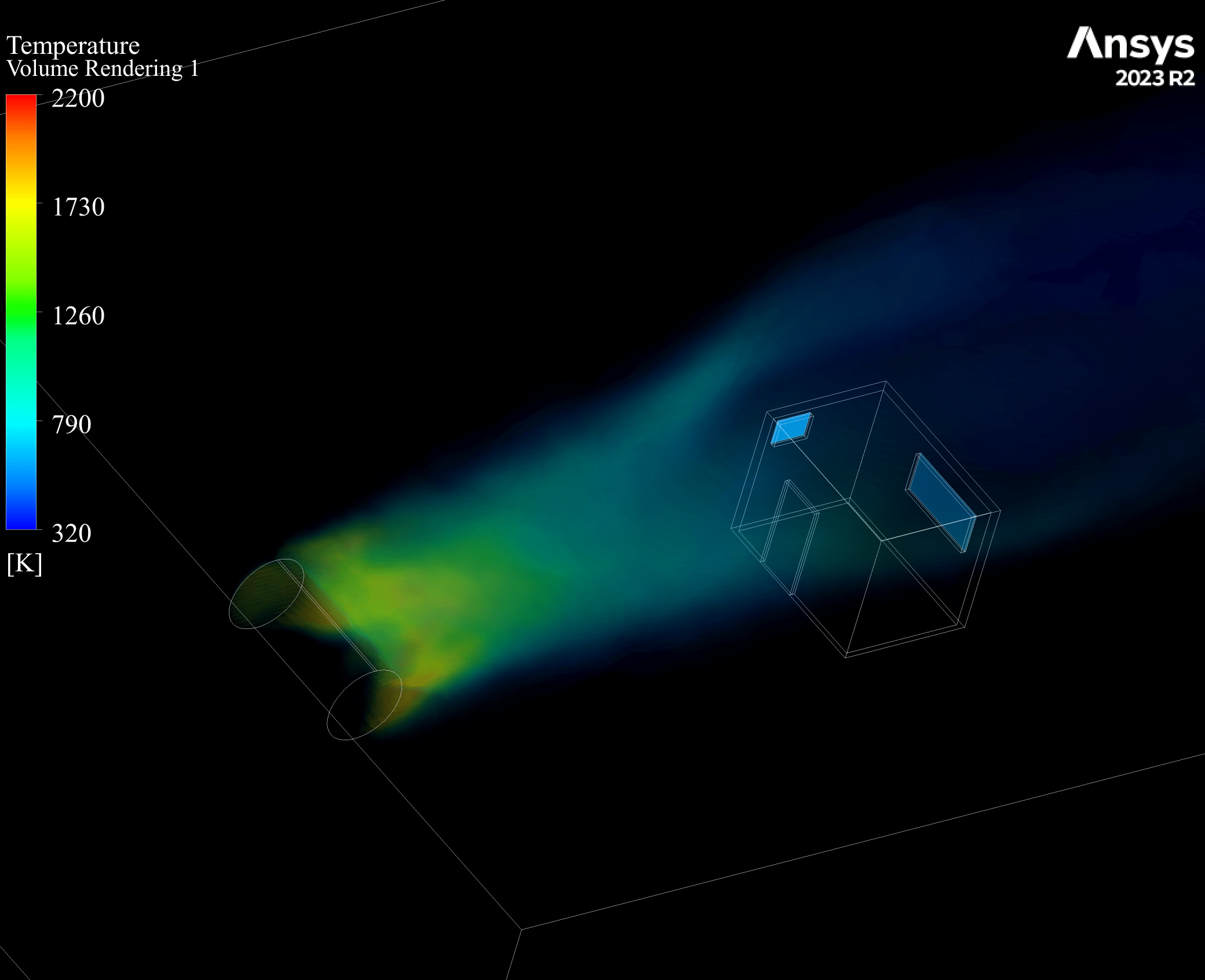
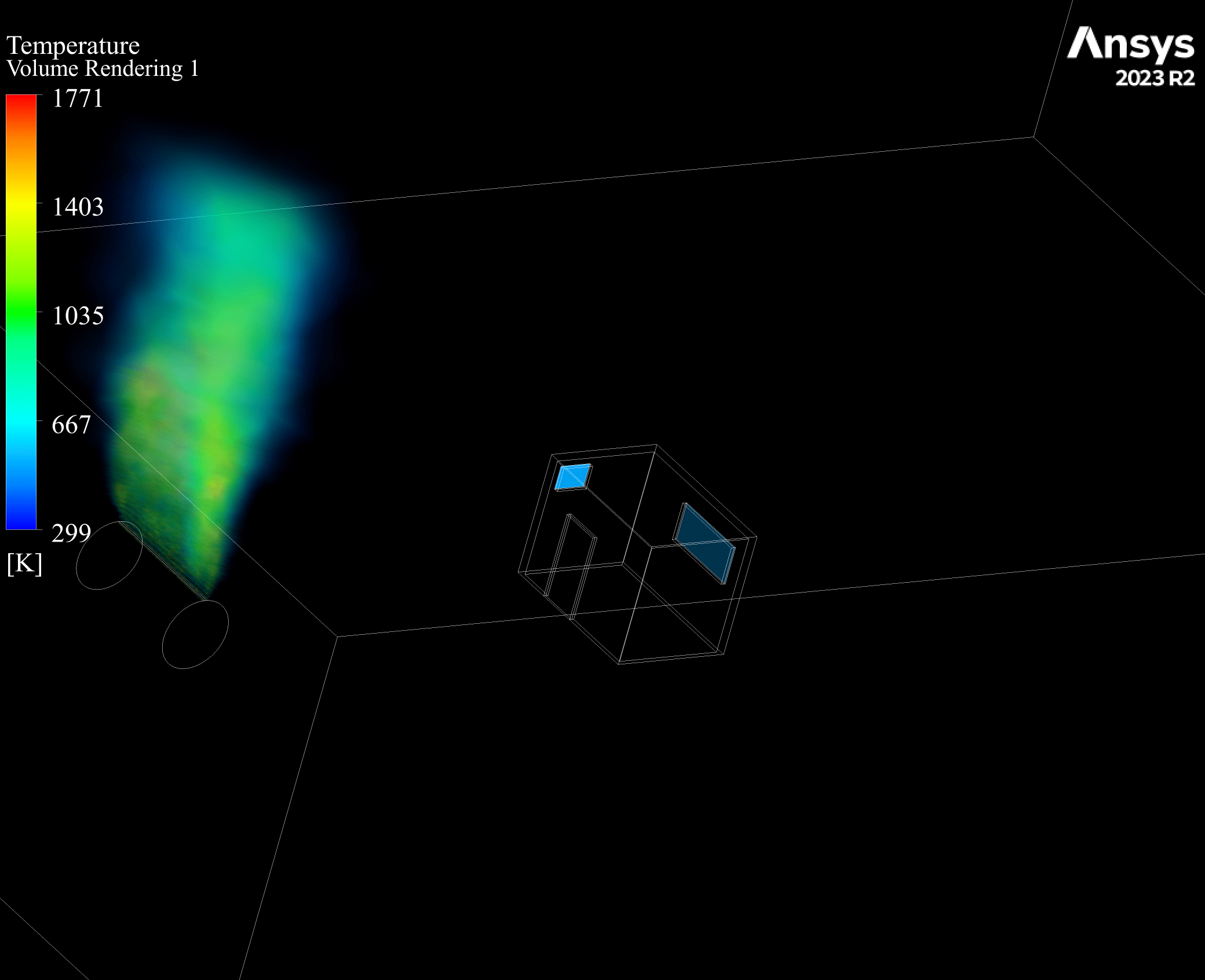
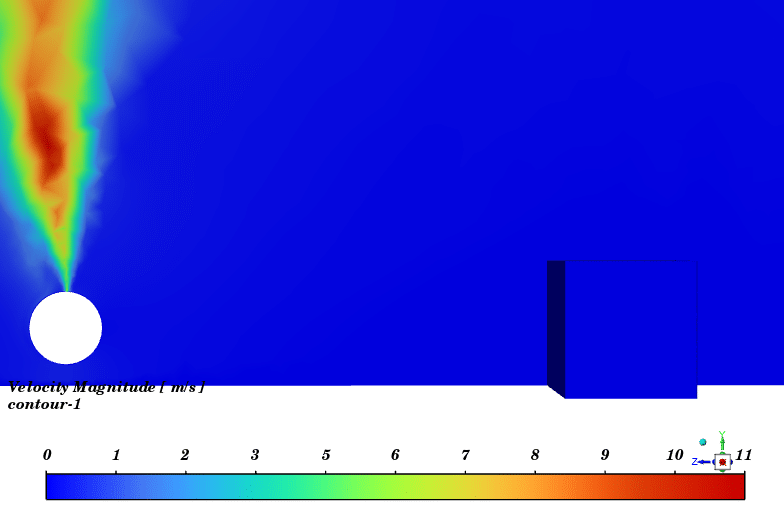
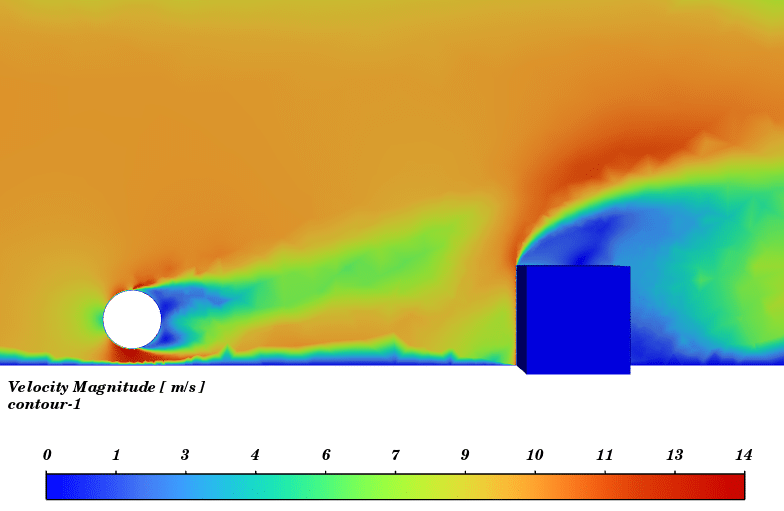
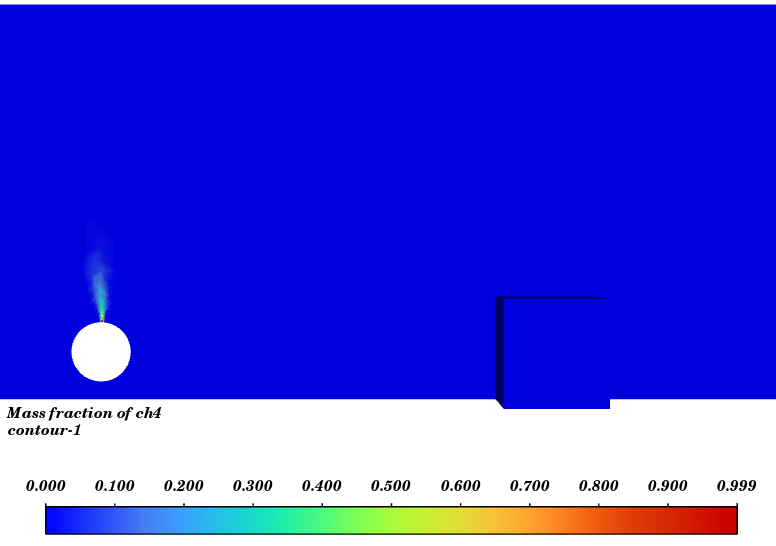
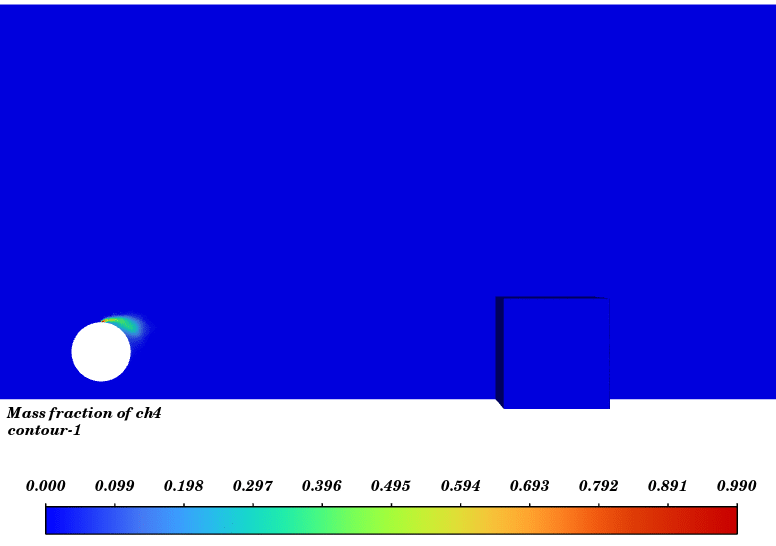
Contours of temperature and species around the fuel tank and room are presented; additionally, 3d contours of temperature are extracted. Average temperature of air inside the room in the case of 10 m/s wind is 330.94K (average temperature of outside building walls is 343.23K) and in the case of no wind the average temperature of air inside the room is 300K.
The initial temperature in this simulation was 300K, and we can see from the results that in the calm weather, because the buoyancy force of hot products is dominant fire goes vertically toward sky and the temperature of room remains without changes but when there is a 10m/s wind toward the room, the free stream momentum of flow is dominant and fire and combustion products pushed toward the building and thermal comfort inside the building is lost. Also, the presence of CO2 reduces air quality.




Reviews
There are no reviews yet.